Adenosine 5′-triphosphate (ATP)
Triphosphate for RNA synthesis and transcription
| Size | Catalog No. | Price |
|---|---|---|
| 1 ml | BCT-42-S | € 60,00 |
| 10 ml | BCT-42-L | € 360,00 |
Chemical Properties
-
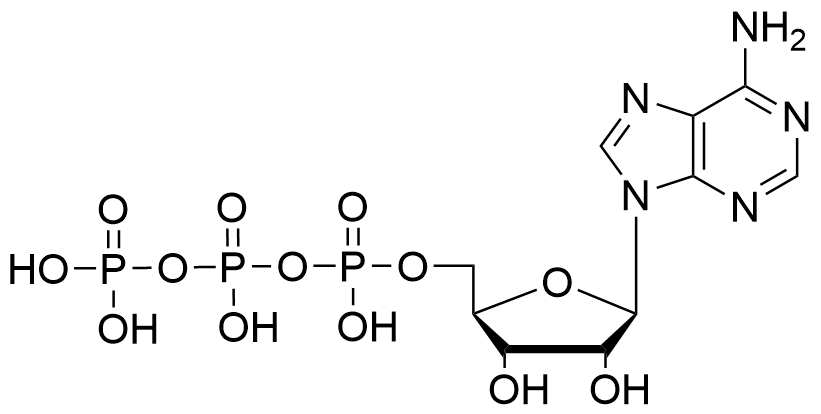
Molecular Formula
C10H16N5O13P3
-
Shelf Life
12 months unopened after receipt
-
Storage Conditions
-20 °C
-
Molecular Weight
507.18 g/mol
-
Purity
≥ 98.5% (HPLC), pH 8.3 ± 0.2
-
Physical State
100 mM solution in water
-
CAS Number
56-65-5 (free acid), 987-65-5 (disodium salt)
-
Absorption (max)
λmax = 260 nm
-
Ɛ (max)
15,000 cm-1M-1 (pH 7.0)
Product Information
The Molecular Engine of Life and Biotechnology
Adenosine 5′-triphosphate (ATP) is a nucleotide made up of an adenine base, a ribose sugar, and three phosphate groups. Often called the “molecular currency of energy,” ATP drives nearly all cellular activities across living organisms from muscle contraction and nerve impulses to biosynthesis, cell division, and membrane transport. In molecular biology, biotechnology, and biomedical applications, ATP isn’t just vital, it’s revolutionary.
ATP as the Central Bioenergetic Molecule
Before ATP was understood, scientists lacked a unifying explanation for energy transfer in cells. Metabolic processes were fragmented, with no clear molecular intermediary.
The discovery and understanding of ATP addressed these challenges and redefined life sciences:
- One molecule for all energy needs: ATP connects and powers nearly every cellular process, from metabolism to gene expression.
- Immediate, usable energy: Its phosphate bonds release energy instantly, fueling cell division, biosynthesis, and active transport.
- Sustainable and regenerable: Recycled via respiration, ATP keeps cells energized without interruption.
- Molecular control switch: Through phosphorylation, ATP activates enzymes and regulates key biological pathways.
Whether you’re advancing biomedical research, developing therapeutics, or running diagnostics ATP is the key driver of precision and performance. Adenosine 5′-triphosphate powers breakthroughs in life science research, diagnostics, and therapeutics.
Applications in Research and Industry
ATP is indispensable across a range of life science fields:
Molecular Biology & Biotechnology
- Powers enzymatic reactions (e.g., ligases, kinases, polymerases)
- Essential in PCR, cell-free protein synthesis, and DNA repair studies
Biomedical Research
- Indicator of cell viability and metabolism
- Foundation for ATP-based luciferase assays in drug discovery and cytotoxicity studies
Diagnostics & Biosensing
- Used in ATP bioluminescence assays for pathogen detection and contamination control
Therapeutics & Cell Therapy
- Studying as a signaling molecule in immune regulation and apoptosis
- Critical for bioenergetics in mitochondrial therapies
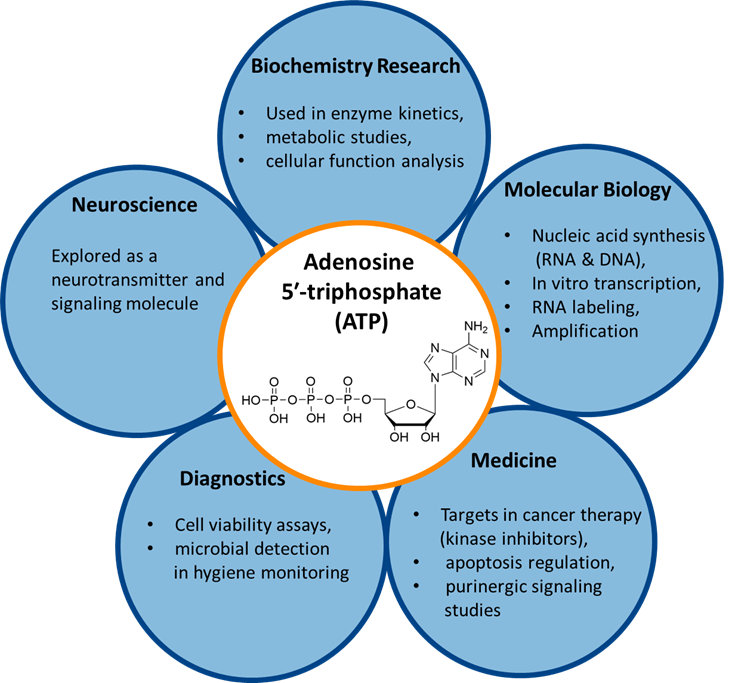
Adenosine 5′-triphosphate isn’t just a compound, it’s the beating heart of biological energy production. From cellular respiration to gene expression, ATP is essential for every living cell and a cornerstone of modern biotechnology and biomedical research. Its versatility as both an energy molecule and signaling molecule empowers discoveries across genomics, therapeutics, diagnostics, and more.

