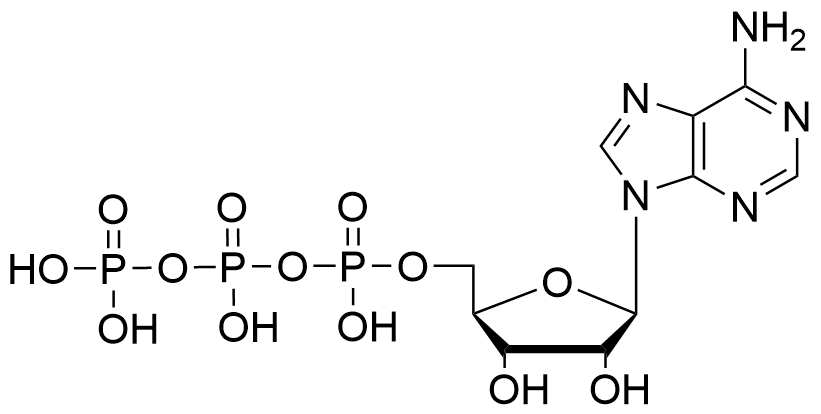
Adenosine 5′-triphosphate (ATP)
Triphosphate for RNA synthesis and transcription
-
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) is a fundamental molecule in the process of RNA synthesis, playing a crucial role in transcription and various RNA-related applications in molecular biology and biotechnology.
RNA Synthesis and Transcription: During transcription, RNA polymerase enzymes synthesize RNA molecules by reading a DNA template. ATP is one of the four ribonucleoside triphosphates (along with GTP, CTP, and UTP) that serve as building blocks for RNA synthesis. ATP provides the adenosine nucleotide that is incorporated into the growing RNA strand. Additionally, the hydrolysis of ATP releases energy that drives the polymerase reaction, enabling the addition of nucleotides to the 3’ end of the RNA molecule.
Energy Transfer: ATP’s role as the universal energy carrier is also vital for the transcription process. The energy released from ATP hydrolysis is used to form the phosphodiester bonds between nucleotides, ensuring the elongation of the RNA strand. This energy transfer is essential for the efficient and accurate synthesis of RNA, which is critical for gene expression and the production of functional RNA molecules.
Applications in Molecular Biology and Biotechnology: In molecular biology, ATP is indispensable for various RNA-related techniques, including in vitro transcription, RNA labeling, and RNA amplification. These techniques are used in gene expression studies, RNA interference (RNAi) experiments, and the development of RNA-based therapeutics. ATP’s involvement in these processes highlights its importance in advancing our understanding of RNA biology and its applications in research and medicine.
By leveraging ATP in RNA synthesis, researchers can explore the complexities of gene regulation, develop novel RNA-based technologies, and enhance the production of RNA molecules for therapeutic purposes. ATP’s critical role in transcription underlines its significance in molecular biology and biotechnology, driving innovation and discovery in the field.
-
-
Molecular Formula
C10H16N5O13P3
-
Shelf Life
12 months unopened after receipt
-
Storage Conditions
-20 °C
-
Molecular Weight
507.18 g/mol
-
Purity
≥ 98.5% (HPLC), pH 8.3 ± 0.2
-
Physical State
100 mM solution in water
-
CAS Number
56-65-5 (free acid), 987-65-5 (disodium salt)
-
Absorption (max)
λmax = 260 nm
-
Ɛ (max)
15,000 cm-1M-1 (pH 7.0)
-
Molecular Formula

