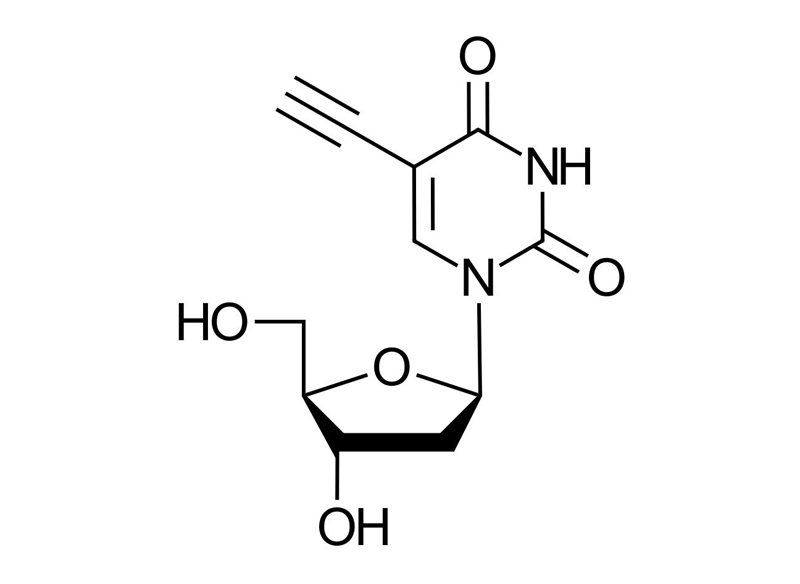
5-Ethynyl-2′-deoxyuridine (5-EdU)
Clickable EdU allows detection of de novo DNA
| Size | Catalog No. | Price |
|---|---|---|
| 50 mg | BCN-001-50 | € 40,00 |
| 100 mg | BCN-001-100 | € 70,00 |
| 500 mg | BCN-001-500 | € 220,00 |
| 1 g | BCN-001-1g | € 375,00 |
Chemical Properties
-
Molecular Formula
C11H12N2O5
-
Shelf Life
12 months unopened after receipt
-
Storage Conditions
-20 °C, dry
-
Molecular Weight
252.23 g/mol
-
Purity
≥ 98% (HPLC)
-
Physical State
white to off-white solid (water content < 0.5 % w/w)
-
CAS Number
61135-33-9
-
Additional name
EdU, 2′-Deoxy-5-ethynyluridine, 5-Ethynyl-1-[(2R,4S,5R)-4-hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]pyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-dione
-
Solubility
DMSO, Alcohol, Water, Aqueous buffers
Product Information
5-Ethynyl-2’-deoxyuridine (5-EdU) a great thymidine analog
baseclick has developed the EdU cell proliferation method based on a thymidine analog, 5-Ethynyl-2’-deoxyuridine (5-EdU) and click chemistry, significantly improving its detection capability. The principle of operation is similar to that of the BrdU (5-bromo-2-deoxyuridine) assay, except for the detection reaction. In summary, the thymidine analogue, in this case EdU (5-ethynyl-2′-deoxyuridine), is also added to the cells and incorporated into newly synthesised DNA during active cell division. This EdU nucleoside contains a reactive alkyne group (instead of the bromine group in BrdU) and is therefore capable of undergoing a so-called click reaction. After an incubation period appropriate for the cell type (comparable to the BrdU procedure), the cells are washed, fixed and permeabilized to allow uptake of the detection reagents. The detection is then performed by the so-called copper-catalysed click reaction (CuAAC). In general, click reactions are reactions that, among other criteria, show high quantitative yields, run under mild reaction conditions, are easy to handle and contain simple starting products. The type of reaction was classified by Nobel Laureates (2022) Barry Sharpless, Carolyn Bertozzi and Morten Meldal. To start the detection reaction, a so-called click cocktail is added to the cells, which contains a fluorophore marker in addition to buffers and catalytic reagents. This fluorophore marker has an azide group that reacts specifically with the incorporated EdU. Only cells that are actively dividing or have already divided contain thymidine analog EdU bases and can be labelled by this method.
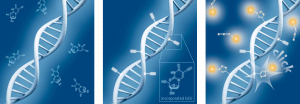
Schematic representation of click chemistry-based EdU cell proliferation assays.
A) Incubation of cells with EdU. B) EdU is incorporated during active DNA synthesis. C) Detection of cell proliferation via click chemistry, wherein the use of a range of different fluorophore marker is possible.
LITERATURE
Template-Directed Oligonucleotide Strand Ligation, Covalent Intramolecular DNA Circularization and Catenation Using Click Chemistry, R. Kumar et al., 2007, J. Am. Chem. Soc., Vol. 129, p. 6859–6864.
https://doi.org/10.1021/ja070273v
A Stepwise Huisgen Cycloaddition Process: Copper(I)-Catalyzed Regioselective “Ligation” of Azides and Terminal Alkynes, V. V. Rostovtsev et al., 2002, Angew. Chemie Int. Ed., Vol. 41, p. 2596–2599.
https://doi.org/10.1002/1521-3773(20020715)41:14<2596::AID-ANIE2596>3.0.CO;2-4
Proliferation and Differentiation of Gastric Mucous Neck and Chief Cells During Homeostasis and Injury-induced Metaplasia, J. Burclaff et al., 2020, Gastroenterology, Vol. 158(3), p. 598-609.
https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2019.09.037
Click Chemistry Generated Model DNA–Peptide Heteroconjugates as Tools for Mass Spectrometry, F. J. Flett et al., 2015, Analytical Chemistry, Vol. 87(19), p. 9595–9599.