EdU Cell Proliferation Assay for Imaging
ClickTech EdU Cell Proliferation Kit for Imaging
| Size | Catalog No. | Price |
|---|---|---|
| Dye 488 / 100 Assays | BCK-EdU488IM100 | 450 € |
| Dye 555 / 100 Assays | BCK-EdU555IM100 | 450 € |
| Dye 594 / 100 Assays | BCK-EdU594IM100 | 450 € |
| Dye 647 / 100 Assays | BCK-EdU647IM100 | 450 € |
-
Cell Analysis – Cell Proliferation Imaging Assays
Cell analysis allows scientists to gain unique insights into cell proliferation, viability, and toxicity, enabling the monitoring of cell response and cell health in cultures after treatment with various stimuli.
Detection of DNA replication is a powerful tool for studying cell proliferation of both cell populations and individual cells. DNA replication can be detected through the incorporation of a nucleoside analog such as BrdU or EdU into DNA. The detection of these two thymidine analogs differs significantly and has implications for test results, potential applications, and multiplexing capability. Compared to the other cell proliferation methods, the EdU proliferation assay does not involve radioactive isotopes or antibodies to detect the newly synthesized DNA.
The ClickTech EdU cell proliferation assay enables estimates of cell proliferation rates by determining the fraction of cells replicating their DNA.The technology is based on the labeling of DNA with EdU (5-ethynyl-2′-deoxyuridine), an alkyne-modified nucleoside that is incorporated into the replicating DNA of living cells and its conjugation to a fluorochrome in situ.
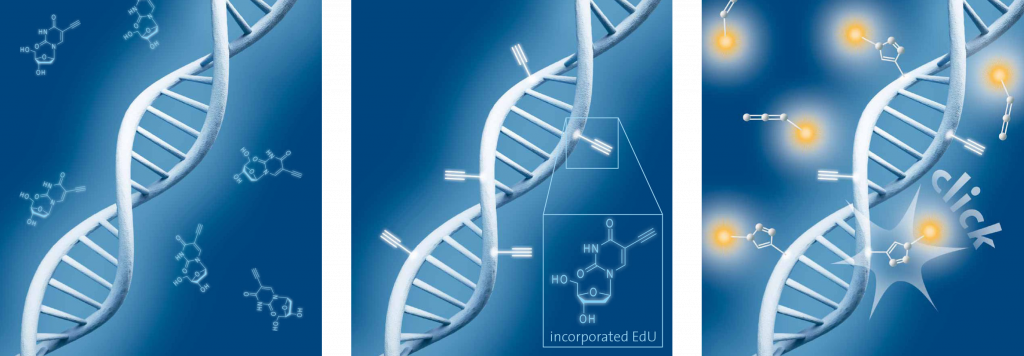
Schematic representation of EdU cell proliferation assays. A) Incubation of cells with EdU. B) EdU is incorporated during active DNA synthesis. C) Detection of cell proliferation via click chemistry, wherein the use of a range of different fluorescent dyes is possible.
Advantages:
- Increased selectivity and sensibility in comparison to BrdU
- Simple, fast and reliable assay
- High sensitivity paired with very low toxicity
- A cost-effective assay
- Multiplexing possibility
- higher preservation of morphological details relative to BrdU
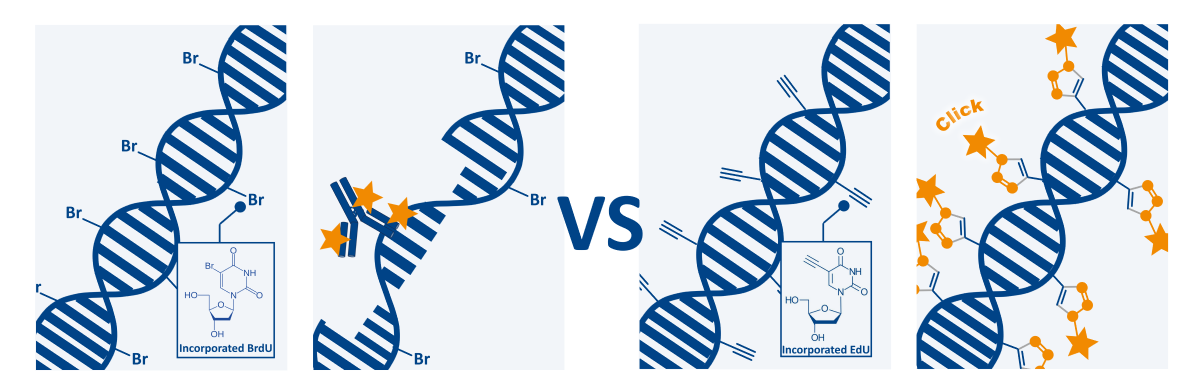
ClickTech EdU Cell Proliferation Assays for Imaging
The baseclick ClickTech EdU cell proliferation assays overcome the limitations of conventional cell proliferation assays and offer a superior alternative to BrdU and [3H] thymidine assays. EdU (5-ethynyl-2′-deoxyuridine) is a thymidine analog, which is incorporated into DNA during active DNA synthesis. The optimized detection protocol considerably simplifies the workflow and the time required. The simple detection procedure is completed within 30 minutes and is compatible with multiplexing for content- and context-rich results.
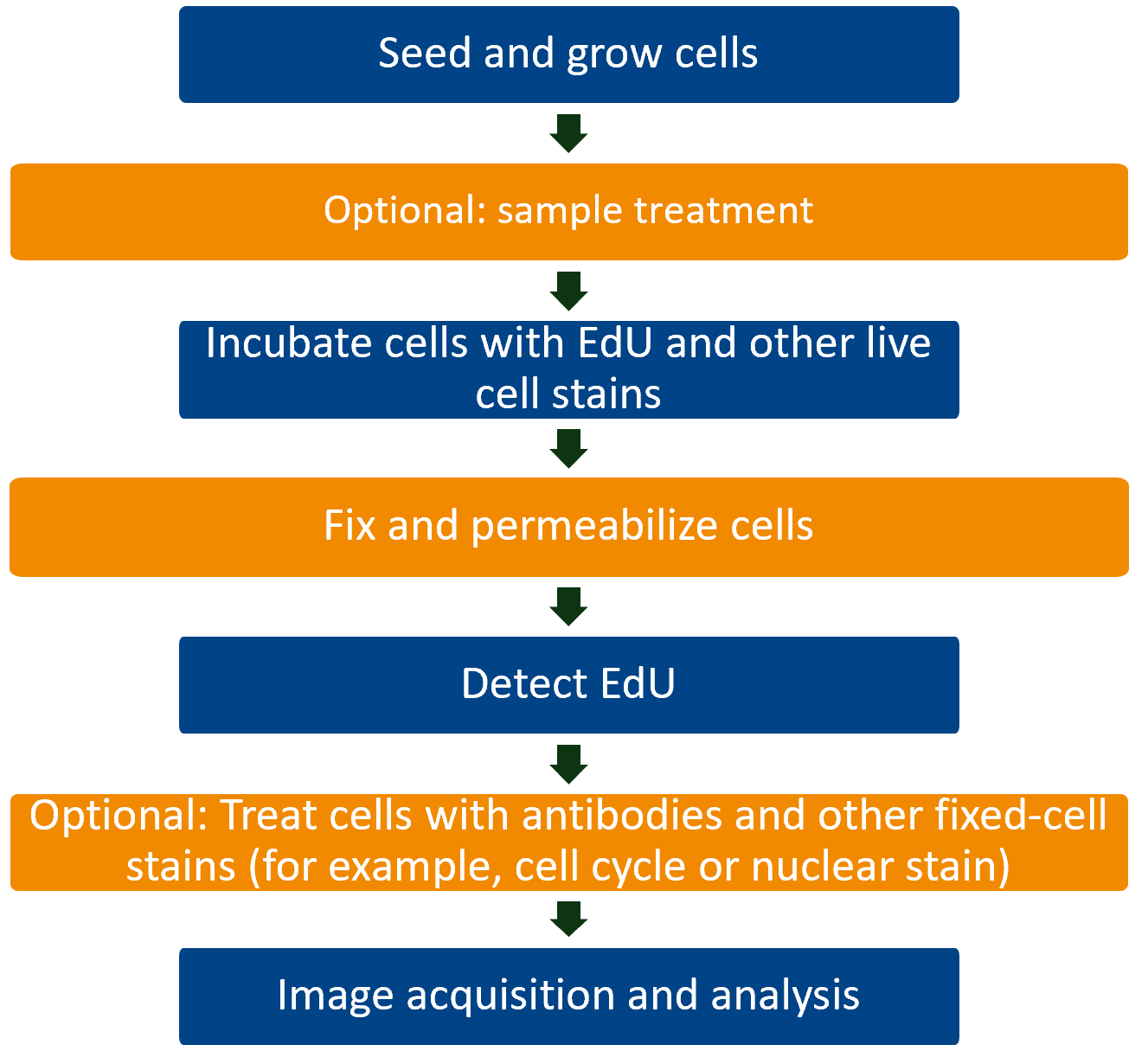
Workflow
EdU Detection
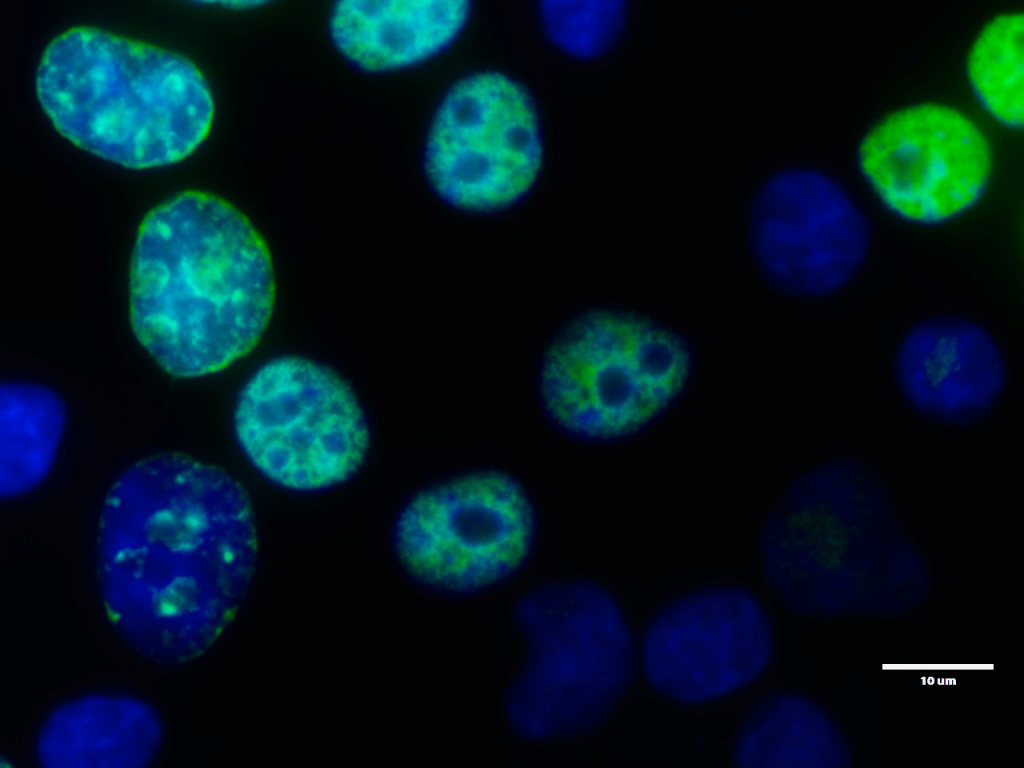
Fluorescence imaging of replicating HeLa cells detected with the EdU Cell Proliferation Kit for Imaging (BCK-EdU488IM100). Green signal: EdU labelling; blue signal: DNA counterstaining with DAPI; scale bar = 10 µm. Distinct replication patterns allow staging of replicating cells along S phase (early/mid/late S phase).
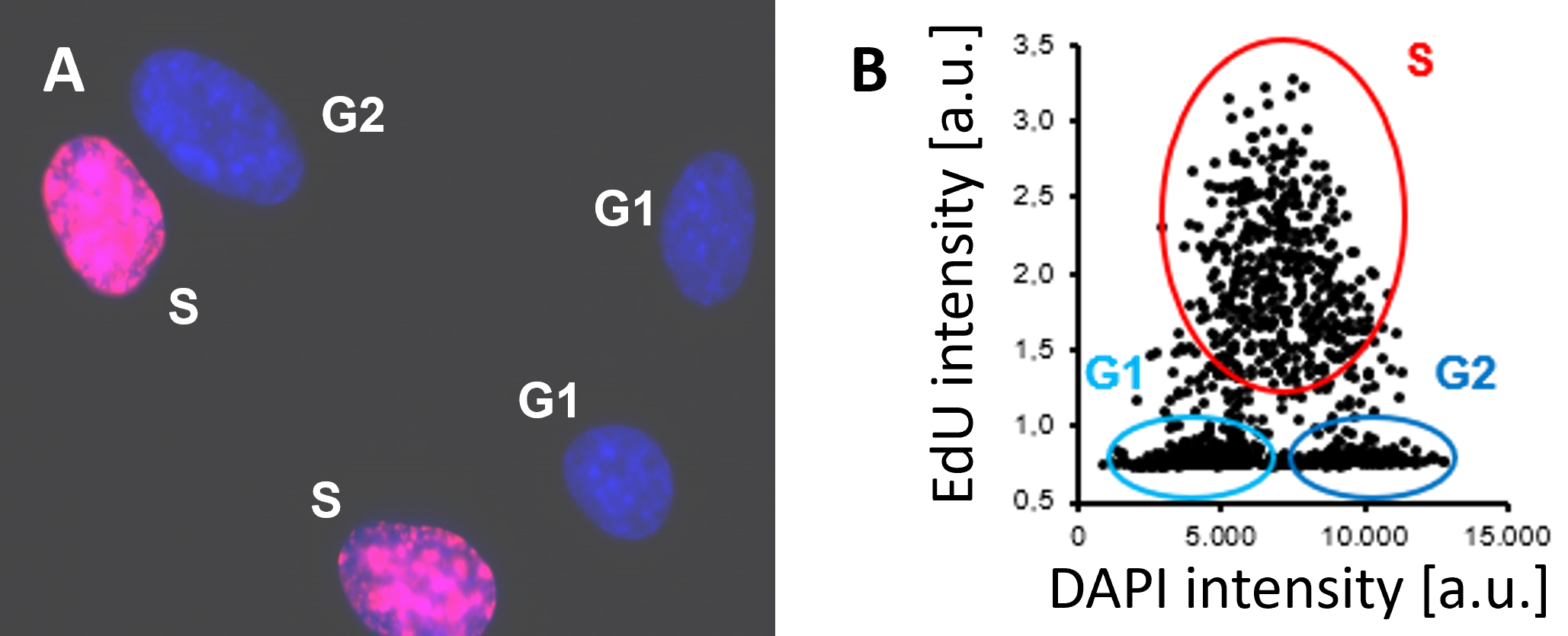
Cell proliferation assay with the EdU Cell Proliferation Kit for Imaging (BCK-EdU647IM100). A) Representative fluorescence microscopy image. Red signal: EdU labelling; blue signal: DNA counterstaining with DAPI. B) Cells in S, G1 and G2/M phases are quantified by image cytometry.
Product Overview
LITERATURE
Anticancer drug and ionizing radiation-induced DNA damage differently influences transcription activity and DDR-related stress responses of an endothelial monolayer, V. Ziegler et al., 2020, Molecular Cell Research, Vol. 1867, p. 118678.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2020.118678
Dendrimer-Based Signal Amplification of Click-Labelled DNA in Situ, N. Raddaoui et al. 2017, ChemBioChem, Vol. 18, p. 1716-1720.
https://doi.org/10.1002/cbic.201700209
High-copy sequences reveal distinct evolution of the rye B chromosome, S. Klemme et al., 2013, New Phytologist, Vol. 199, p. 550-558.
https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.12289
Cytolethal Distending Toxin Promotes Replicative Stress Leading to Genetic Instability Transmitted to Daughter Cells, W. Tremblay et al., 2021, Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology, Vol. 9, 656795.
https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2021.656795
Brassica napus Roots Use Different Strategies to Respond to Warm Temperatures, M. Boter et al., 2023, Int. J. Mol. Sci., Vol. 24(2), 1143.
FAQ
-
What type of cells can incorporate EdU?
The EdU cell proliferation assay has been applied to many different cell types and organisms from prokaryotic to eukaryotic. Cell lines such as E. coli, HeLa, HEK, MOLM are arguably among the most routine applications, but also animals, like mouse, rat, the nematode C. elegans, crickets (Gryllus bimaculatus), chicken (Gallus domesticus) and zebra fish (Danio rerio) or even plants (e.g. Arabidopsis thaliana) can be applied.
Cells that possess a pyrimidine pathway that can phosphorylate EdU to the corresponding triphosphate, which is then accepted by the host DNA polymerase for incorporation into DNA during replication. -
Can I perform EdU cell proliferation detection on living cells?
EdU is incorporated into living cells, but the detection reaction must be performed on fixed and permeabilized samples.
-
How does EdU labeling compare to BrdU or the 3H-thymidine incorporation assay?
All three methods enable to determine cell proliferation directly by incorporation of a metabolite analogue and subsequent detection. The 3H-thymidine incorporation assay is very sensitive, but the radioactive compound requires specialized equipment and dedicated lab space for handling. EdU and BrdU assays are non-radioactive alternatives with decreased risk for health and environment. Compared to the BrdU incorporation assay the EdU assay is more sensitive, requires less handling time and needs no harsh DNA denaturing conditions for detection. Therefore, the EdU cell proliferation is also compatible with multiplexing.
-
Can I combine DAPI staining and EdU detection?
Yes, this is feasible. Please note that DAPI staining should be done after the click detection step. Alternatively, SYBR Green DNA staining can be used. But, please note that SYBR green should not be used with dyes of 488 nm wavelengths.
-
When can I safely interrupt the experiment?
It is possible to safely interrupt the protocol after the fixation step. Thereto, remove the fixation solution and wash as suggested by the user manual, then the cells can be stored in buffer at 4° C. Alternatively, the experiment can also be safely interrupted after permeabilization, again as described above.
Please note: It is important to proceed with the experiment if the click cocktail for the detection of the EdU has been prepared already. -
Is antibody staining compatible with the EdU?
Antibody staining is compatible with EdU cell proliferation detection when antibody detection is done after the click detection step. Please be aware of the dye used for EdU detection. Check also the user manual for more information.
-
How to determine the EdU incubation time?
The EdU incubation time depends on the cell type or organism, the applied EdU concentration and the experimental design. For a start it is advisable to refer to a literature protocol (which is close to your experimental setup) and to test the conditions with a low number of samples. As a general guideline we recommend to use a maximum of 10 µM final EdU in the cell culture medium for incubations. For longer incubation (> 1 day) the concentration should be decreased to 1-5 µM.
-
-
Shelf Life
12 months unopened after receipt
-
Storage Conditions
2-8 °C
-
Physical State
kit system made of different components
-
CAS Number
n.a.
-
Excitation (max)
Dye 488: 496 nm | Dye 555: 546 nm | Dye 594: 584 nm | Dye 647: 643 nm
-
Emission (max)
Dye 488: 516 nm | Dye 555: 579 nm | Dye 594: 603 nm | Dye 647: 662 nm
-
Ɛ (max)
Dye 488: 83.000 cm-1M-1 | Dye 555: 91.000 cm-1M-1 | Dye 594: 110.000 cm-1M-1 | Dye 647: 250.000 cm-1M-1
-
Preparation/Handling
please see user manual of the kit
-
Shelf Life

