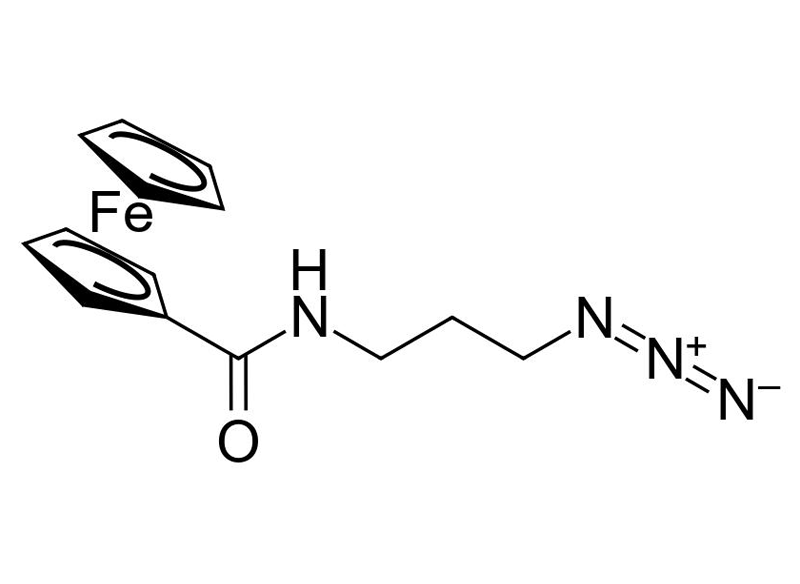
Ferrocene Azide
Organometallic tag for labeling DNA/RNA
| Size | Catalog No. | Price |
|---|---|---|
| 5 mg | BCFA-019-5 | € 170,00 |
| 10 mg | BCFA-019-10 | € 300,00 |
-
Ferrocene is a so-called sandwich complex consisting of an central iron (II) ion and two cyclopentadienyl rings on opposite sides. The azido modification allows this compound to be bond to any alkyne-/DBCO-modified biomolecule by click chemistry.
The ability to oxidize this complex to ferrocenium makes it an ideal marker for electrochemical detection (EC probes). For example, ferrocene modified oligos can be detected with HPLC-ECD methods in the sub-femtomole range. Due to these properties, EC probes have the potential to be a cost-effective alternative to fluorescence-based probes in clinical or medical diagnostic, e.g. for DNA microarray systems.
In a recent study, ferrocene azide was also used for the development of electrochemical biosensors based on graphene nanoribbons. Additionally, ferrocene shows high stability against heat, basic pH and hydrolysis which enables subsequent reactions or long-time storage. An advantage in contrast to fluorescent labeled oligos, which are slowly destroyed after detection. Ferrocene-modified oligos can be analyzed or measured more frequently.
LITERATURE
Electrochemically active DNA probes: Detection of target DNA sequences at femtomole level by high-performance liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection, S. Takenaka et al. 1994, Anal. Biochem., 218: 436-443.
https://doi.org/10.1006/abio.1994.1203
Ferrocene-oligonucleotide conjugates for electrochemical probing of DNA T. Ihara et al., 1996, Nucleic Acids Res., 24: 4273-4280.
https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/24.21.4273
DNA-arrays with electrical detection: A label-free low cost technology for routine use in life sciences and diagnostics. P. Liepold et al., 2005, Bioelectrochem., 67: 143-150.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioelechem.2004.08.004
Electrically detected displacement assay (EDDA): a practical approach to nucleic acid testing in clinical or medical diagnosis, P. Liepold et al., 2008, Anal. Bioanal. Chem., 391: 1759-1772.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-008-2045-5
Interface Engineering of “Clickable” Organic Electrochemical Transistors toward Biosensing Devices Devices, G. E. Fenoy et al., 2023, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, Vol. 15(8), p. 10885–10896.
https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.2c21493
“Clickable” graphene nanoribbons for biosensor interfaces, R. Hasler et al., 2024, Nanoscale Horiz., 9, 598-608.
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3NH00590A
-
-
Molecular Formula
C14H16FeN4O
-
Shelf Life
12 months unopened after receipt
-
Storage Conditions
-20 °C, dry, inert gas
-
Molecular Weight
312.15 g/mol
-
Purity
≥ 98% (HPLC)
-
Physical State
yellow to light orange solid
-
CAS Number
1887761-56-9
-
Solubility
DMSO
-
Preparation/Handling
For a 10 mM solution add 320 μL to 1 mg.
-
Molecular Formula

