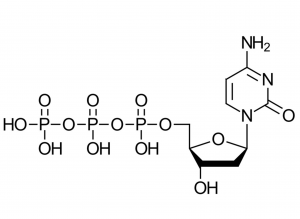
What is dCTP? An Overview of Deoxycytidine Triphosphate
Definition of dCTP
dCTP is one of the four deoxynucleotide triphosphates (dNTPs) that form the building blocks of DNA. These molecules are essential for DNA synthesis and replication, providing the necessary components for constructing DNA strands. dCTP consists of a deoxyribose sugar, a cytosine base, and three phosphate groups.
Chemical Structure of dCTP
dCTP consists of a deoxyribose sugar, a cytosine base, and a triphosphate group.
The deoxyribose forms the sugar backbone, while the cytosine is a pyrimidine base that pairs with guanine in the DNA doublestrand.
The triphosphate group is crucial for providing the energy required for DNA synthes
Function of dCTP
dCTP plays an important role as a precursor in DNA synthesis.
Basic Function
- During DNA replication and repair, dCTP is incorporated into the DNA strand by DNA polymerases. These enzymes add dCTP to the growing DNA chain, ensuring the correct sequence is maintained.
- The triphosphate group of dCTP is crucial, as it provides the necessary energy for the nucleotide to be successfully added to the expanding DNA strand, facilitating the elongation process.
Role of dCTP in DNA Synthesis
dCTP is essential in both the replication and repair of DNA, maintaining the genetic integrity of an organism. During DNA replication, dCTP serves as a critical building block for extending the DNA chain. DNA polymerases, the enzymes responsible for synthesizing new DNA strands, incorporate dCTP along with other deoxynucleotide triphosphates (dNTPs) into the growing DNA strand by forming phosphodiester bonds. The triphosphate group of dCTP provides the necessary energy for the formation of these bonds, ensuring the continuous elongation and stability of the DNA strand. In addition to its role in replication, dCTP is also vital for DNA repair. It plays a key role in maintaining genetic stability by participating in DNA repair mechanisms, such as nucleotide excision repair. In these processes, dCTP is utilized to replace damaged or mismatched cytosines, ensuring the integrity and accuracy of the DNA sequence is preserved.
Applications of dCTP
dCTP has a wide range of applications in molecular biology, particularly in DNA amplification, sequencing, and various research techniques.
PCR and Sequencing
dCTP is a crucial component in the Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR), a technique used to amplify DNA. During PCR, dCTP is one of the nucleotides added by DNA polymerases to replicate the target DNA sequence. It is also essential in next-generation sequencing technologies, playing a role in the synthesis of complementary DNA (cDNA) and in the preparation of DNA libraries.
Fluorescently labeled dNTPs, including dCTP, are critical in sequencing technologies. These labeled nucleotides enable the detection of specific DNA sequences by special detection systems in sequencing machines. Each nucleotide emits a unique fluorescent signal, which allows for high-precision DNA sequencing. Click chemistry enhances these processes by enabling efficient and high-yield fluorescent labeling of dCTPs and other dNTPs, making it a valuable tool for effective sequencing techniques.
NGS Library Preparation
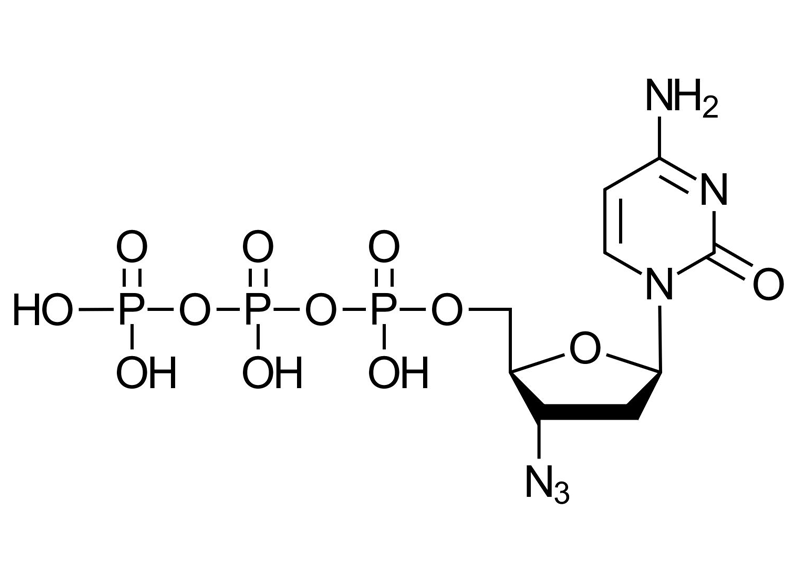
Azido-2′,3′-ddCTP , a modified form of dCTP, is utilized in specialized enzymatic assays, such as those based on ClickSeq technologies. It is used to induce random stops in cDNA synthesis, which leads to the generation of diverse libraries from RNA pools. This technique is crucial for creating comprehensive libraries in cDNA synthesis for further genetic analysis.
Research and Diagnostics
dCTP is extensively used in genetic research and diagnostic applications. It is fundamental in various molecular biology techniques, including DNA labeling, sequencing, and genotyping, where it helps in analyzing genetic material and diagnosing genetic conditions.
Modifications of dCTP for Advanced Research Applications.
Azido-2′,3′-ddCTP
Azido-2′,3′-ddCTP is an innovative nucleotide modification for mRNA labeling. It is an azide-modified nucleotide that closely resembles natural nucleotides, making it suitable for chemoenzymatic mRNA labeling. Due to the small size of the azide group, this modified nucleotide is readily accepted by enzymes like T7 RNA polymerase and terminal deoxynucleotidyltransferase (TdT). This enables site-specific labeling of mRNA at the 3′-end without needing bulky, pre-labeled nucleotides. Azido-2′,3′-ddCTP has proven highly versatile, successfully modifying RNA for downstream analyses and functional studies
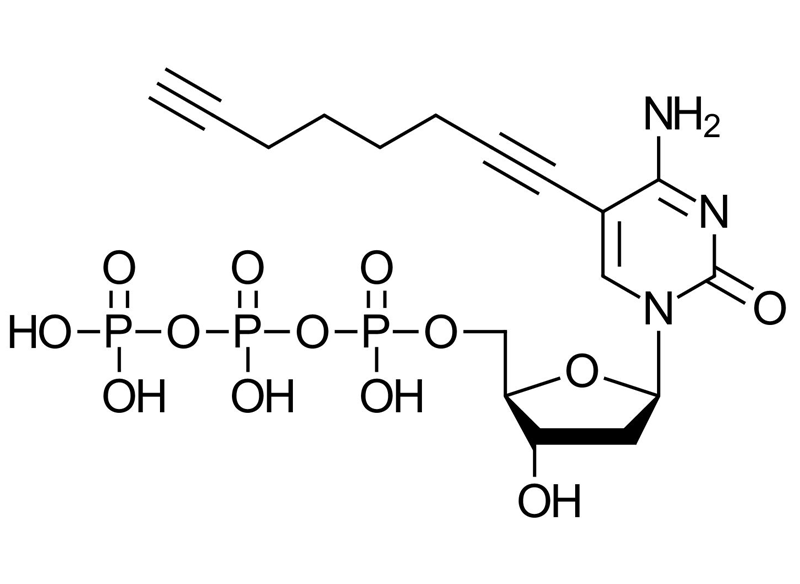
C8-alkyne-dCTP
C8-alkyne-dCTP is another modified nucleotide used for the functionalization of DNA through click chemistry. This nucleotide can be easily incorporated into DNA during PCR using polymerases such as Pwo, Deep Vent exo-, or KOD XL. By substituting 1-10% of natural dCTP with C8-alkyne-dCTP, researchers can create DNA fragments that are primed for further functionalization via click chemistry. This method allows the introduction of additional chemical groups into the DNA, enabling advanced labeling, immobilization, or conjugation reactions for a variety of downstream applications.
Importance of dCTP
dCTP holds a vital place in molecular biology due to its essential role in DNA synthesis, replication, and repair. It is indispensable in its natural form, but its modified variants also provide significant value for research and biotechnology applications.
Research Potential
dCTP is a critical component in studying genetic mechanisms. Its involvement in DNA synthesis and repair makes it an important tool for understanding fundamental genetic processes, such as mutation rates, genomic stability, and DNA-protein interactions.
Moreover, modified versions of dCTP, like azido-2′,3′-ddCTP and C8-alkyne-dCTP, further expand its utility in research. Azido-2′,3′-ddCTP allows for precise labeling of DNA or RNA molecules, while C8-alkyne-dCTP facilitates advanced functionalization of DNA. These modifications enable more complex studies and applications in molecular biology, such as tracking molecular interactions or creating specialized DNA constructs for biotechnological purposes.
Availability and Laboratory Use
Commercial Products
dCTP is commercially available as a reagent in various concentrations and purity levels to meet the diverse needs of scientific research. It is provided in multiple concentrations to accommodate different laboratory applications, ranging from low concentrations for precise and controlled experiments to higher concentrations for large-scale procedures, such as PCR and high-throughput sequencing.
Commercial Products: Both the natural form of dCTP and its modified variants are offered as commercial products, with varying degrees of purity suitable for different scientific applications. High-purity dCTP is crucial for ensuring accurate and reliable results in molecular biology experiments, including PCR, DNA sequencing, and diagnostic testing.
In addition to its natural form, modified versions of dCTP, such as Azido-2′,3′-ddCTP and C8-Alkyne-dCTP, are also available. These modified forms are designed for specific research applications, such as DNA labeling and modification, providing researchers with the tools necessary for advanced genetic studies and molecular investigations.