
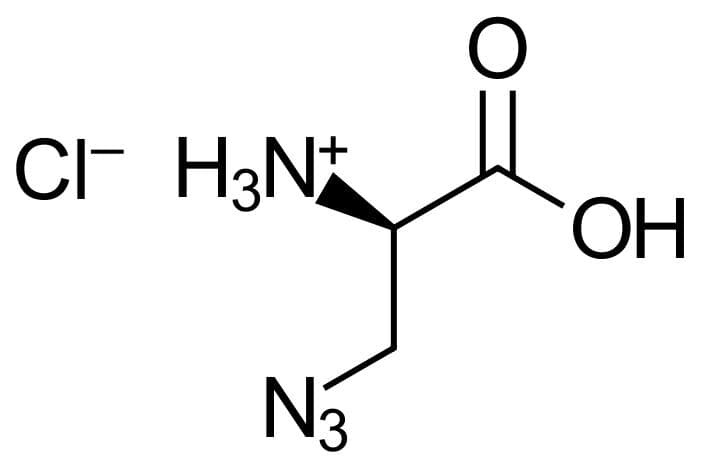
3-Azido-D-alanine HCl
Azido-modified amino acids for bioconjugation with alkyne reporters
| Size | Catalog No. | Price |
|---|---|---|
| 100 mg | BCAA-004-100 | € 150,00 |
Chemical Properties
-
Molecular Formula
C3H6N4O2 *HCI
-
Shelf Life
12 months unopened after receipt
-
Storage Conditions
2-8 °C, dry, hygroscopic!
-
Molecular Weight
130.11 g/mol * 36.45 g/mol
-
Purity
≥ 98% (HPLC)
cristal water content 8-11%
-
Physical State
white to off-white crystalline powder
-
CAS Number
1379690-01-3 (hydrochloride salt)
105928-88-9 (free acid) -
Additional name
H-D-Aza-OH *HCl; H-D-Dap(N3)-OH*HCl; H-D-Ala(N3)-OH*HCl; 3-Azido-D-alanine hydrochlorid; (R)-2-Amino-3-azidopropanoic acid hydrochlorid
Product Information
Stable and Bioorthogonal Protein Labeling with D-Amino Acid Technology
3-Azido-D-alanine hydrochloride ((R)-2-Amino-3-azidopropanoic acid hydrochloride) is a synthetic, unnatural D-amino acid derivative of alanine carrying an azide group. It enables site-specific protein modification and bioorthogonal labeling via Click Chemistry (SPAAC or CuAAC) or Staudinger ligation under mild conditions.
This reagent can be incorporated into peptides or proteins through:
- Genetic Code Expansion: Using engineered tRNAs (based on prokaryotic tRNAs) that recognize amber codons as UAG, therefore 3-Azido-D-alanine is introduced during biosynthesis at a defined position (1) .
- Solid Phase Peptide Synthesis (SPPS): Allows chemical incorporation at any position in the peptide sequence.
Once incorporated, the azide moiety reacts selectively with alkyne-modified partners (alkynes, DBCO, BCN) or P(III)-containing reagents, enabling efficient conjugation without side reactions.
Why choose 3-Azido-D-alanine?
Traditional labeling methods rely on NHS ester chemistry, which reacts with primary amines (e.g., lysines) and leads to:
- Non-specific labeling at multiple sites.
- Requires basic pH (8–9) and overnight reactions.
- Risks protein degradation and structural changes.
In contrast, azide-based labeling with 3-Azido-D-alanine offers:
- Site-specific modification at the planned position.
- Fast reactions at neutral pH with high yields.
- Preserves tertiary structure.
- Fully bioorthogonal—no interference with native functional groups.
- Lower reagent consumption and atom-economic click chemistry for cost-effective, eco-friendly workflows.
Unique Benefits of D-Amino Acid Incorporation
- Increased stability: Peptides containing D-amino acids resist enzymatic degradation by proteases and peptidases.
- Structural variation: D-amino acids alter peptide folding (e.g., preventing α-helix formation), enabling novel structural designs for research and drug development.
Applications of 3-Azido-D-alanine HCl in Protein Engineering
3-Azido-D-alanine is a powerful tool for protein and peptide labeling, enabling precise site-specific modification through bioorthogonal click chemistry. It is widely used for antibody modification and ADC synthesis, supporting the development of targeted therapeutics. Researchers also rely on this reagent for linking targeting moieties to proteins in drug delivery and diagnostic applications. Additionally, its compatibility as a building block for solid-phase peptide synthesis (SPPS) makes it ideal for custom peptide design in pharmaceutical development, biotechnology, and advanced biochemistry workflows.
LITERATURE
1. Incorporating unnatural amino acids into recombinant proteins in living cells, Mitra, N., 2013, Materials and Methods, Vol. 3, p.204, 1.
http://doi.org/10.13070/mm.en.3.204
2. Mapping the Ligand-Binding Site on a G Protein-Coupled Receptor (GPCR) Using Genetically Encoded Photocrosslinkers, Grunbeck et al., 2011, Biochemistry, Vol. 50, p. 3411-3413.
https://doi.org/10.1021/bi200214r
3. Azide click chemistry on magnetotactic bacteria: A versatile technique to attach a cargo, P. E. D. S. Rodriguez et al., 2023, Materials Today Bio, Vol. 19, 100587.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtbio.2023.100587
4. Novel Chromosome Organization Pattern in Actinomycetales—Overlapping Replication Cycles Combined with Diploidy, K. Böhm et al., 2017, MBio, Vol. 8(3), p. 10-1128.
https://doi.org/10.1128/mbio.00511-17
5. Azide click chemistry on magnetotactic bacteria: a versatile technique to attach a cargo, Soto, P., Sirinelli-Kojadinovic, M., Rouzaud, M., & Faivre, D., 2022, Chemrxiv.
https://doi.org/10.26434/chemrxiv-2022-dtb1t
FAQ
-
Is it possible to generate azide- or alkyne-modified peptides?
With modified amino acids azide- or alkyne-modified peptides can be prepared by solid-phase synthesis.
-
How can de novo protein biosynthesis be monitored?
De novo protein biosynthesis can be monitored by feeding of metabolite analogues (so-called metabolic labeling) and subsequent click reaction. Azido-homoalanine for example is recognized as a methionine analogue and is incorporated into de novo synthesized proteins in methionine-free medium conditions. The resulting proteins contain azide moieties and thus can be detected after click to an alkyne-containing reporter molecule (e.g. a fluorescent dye). This non-radioactive method has major practical advantages compared to traditional 35S amino acid incorporation methods.
Alternatively, O-propargyl-puromycin is efficiently incorporated into proteins during de novo protein biosynthesis and can be used in complete medium. The resulting alkyne protein fragments can be detected via click to azide-containing reporter molecules. -
What click conditions should be used for protein click reactions?
A catalyst system based on CuSO4 and sodium ascorbate is recommended in combination with dye azides to label alkyne-modified proteins. Please also refer to our general Click protocols for more details.
Due to the 20 (21) amino acids that are the building blocks of proteins, the physicochemical properties of proteins are more diverse compared to oligonucleotides, which are just composed of 5 major building blocks. Therefore, finding the optimal click conditions is more difficult compared to oligonucleotides and labeling rates are usually lower. Please note that despite these difficulties detection applications (e.g. de novo protein biosynthesis detection) are easily feasible. -
Why use 3-Azido-D-alanine instead of NHS ester chemistry?
It provides precise, site-specific labeling under mild conditions, avoiding multiple modification sites and preserving protein integrity.
-
Which click reactions are supported?
SPAAC (copper-free) and CuAAC (copper-catalyzed) for rapid, efficient conjugation.
-
Does the D-configuration matter?
Yes. D-amino acids increase peptide stability and alter tertiary structure, making them ideal for specialized applications.
-
Can it be used in solid-phase peptide synthesis (SPPS)?
Yes, it can be incorporated at any position during peptide synthesis.
-
What labeling partners are compatible?
Alkyne/DBCO/BCN-modified PEGs, fluorescent dyes, antibodies, and targeting moieties.

