
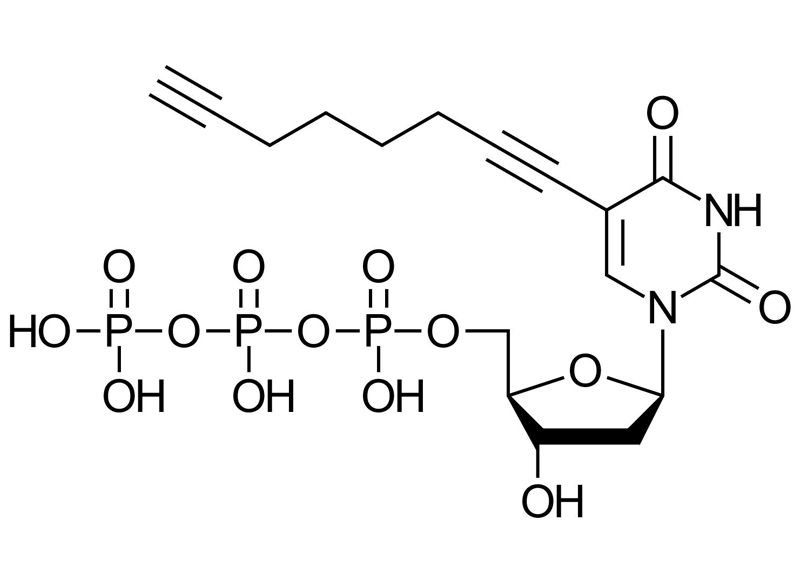
C8-Alkyne-dUTP
Modified triphosphate for incorporation in PCR reaction
| Size | Catalog No. | Price |
|---|---|---|
| 1 µmol | BCT-05-S | € 100,00 |
| 5 µmol | BCT-05-L | € 300,00 |
Chemical Properties
-
Molecular Formula
C17H23N2O14P3
-
Shelf Life
12 months unopened after receipt
-
Storage Conditions
-20 °C
-
Molecular Weight
572.29 g/mol
-
Purity
≥ 95% (HPLC)
-
Physical State
100 mM clear colorless
solution in water (pH 7.5) -
CAS Number
1004297-65-7 (free acid)
-
Absorption (max)
λmax = 292 nm
-
Ɛ (max)
11.000 cm-1M-1
Product Information
A Click-Functionalized Nucleotide for DNA Labeling and Post-Synthetic Modification
C8-Alkyne-dUTP is a modified deoxyuridine triphosphate (dUTP) featuring a C8 alkyne group at the C5 position of the uracil base. It enables site-specific DNA labeling via Cu(I)-catalyzed azide-alkyne cycloaddition (CuAAC), supporting a wide range of downstream applications in molecular biology, diagnostics, and nanobiotechnology.
The Molecular Engine for DNA Functionalization and Bioorthogonal Chemistry
C8-Alkyne-dUTP introduces a chemically orthogonal alkyne moiety into DNA during enzymatic synthesis. This modification allows for precise post-synthetic conjugation with azide-bearing molecules, including fluorophores, biotin, peptides, and other functional groups. It is designed to overcome limitations in traditional nucleotide labeling strategies and expand the toolkit for DNA-based technologies.
Challenges in DNA Labeling and Modification
Prior to the development of click-functionalized nucleotides, researchers faced several limitations:
- Polymerase Compatibility
Many modified nucleotides were poorly tolerated by DNA polymerases, resulting in inefficient incorporation. - Limited Functional Labeling Options
Conventional dUTPs lacked reactive groups for selective post-synthetic modification. - Non-Specific Conjugation Chemistry
Labeling often relied on NHS esters or maleimides, which lacked positional control and reproducibility.
C8-Alkyne-dUTP as a Bioorthogonal Solution
- Click-Ready Functionality
The terminal alkyne group enables selective and efficient CuAAC reactions with azide-functionalized probes under mild conditions. - High Incorporation Efficiency
The C8 modification is positioned on the nucleobase, away from the polymerase active site, allowing incorporation by Taq, KOD, Vent, Pwo, and Deep Vent exo- polymerases. - Versatile Post-Synthesis Labeling
Once incorporated, the alkyne-modified base can be conjugated to a wide range of azide-bearing molecules without disrupting DNA structure or function.
Applications in Research and Biotechnology
- DNA Labeling
Enables site-specific modifications for imaging, purification, and molecular tracking. - Biotinylation and Affinity Tagging
Facilitates streptavidin-based capture and purification of labeled DNA strands. - PCR and Primer Extension
Compatible with enzymatic incorporation for advanced genetic studies. - DNA Nanotechnology
Supports spatially controlled modification of DNA origami and nanostructures. - Oligonucleotide–Drug Conjugates
Enables site-specific attachment of small molecules or peptides for therapeutic and diagnostic use. - Gene Silencing
Enhances triplex-forming oligonucleotides (TFOs) with improved stability and gene-targeting efficiency. - DNA Hydrogel Functionalization
Allows post-synthetic modification of DNA hydrogels via CuAAC without compromising mechanical properties. - Aptamer Discovery
Used in Click-Particle Display for screening base-modified aptamers with enhanced binding properties. - dNTP Quantification
Provides a safer alternative to radioisotope-based assays using fluorophore conjugation.
LITERATURE
Synthesis of Highly Modified DNA by a Combination of PCR with Alkyne-Bearing Triphosphates and Click Chemistry, J. Gierlich et al., 2007, Chem. – A Eur. J., Vol. 13, p. 9486–9494.
https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.200700502
Directed DNA Metallization, G. A. Burley et al., 2006, J. Am. Chem. Soc., Vol. 128, p. 1398–1399.
https://doi.org/10.1021/ja055517v
Fluorescent labelling of in situ hybridisation probes through the copper-catalysed azide-alkyne cycloaddition reaction, S. Hesse et al., 2016, Chromosome Research, Vol. 24(3), p. 299–307.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s10577-016-9522-z
Enzymatic Synthesis of Chemical Nuclease Triplex-Forming Oligonucleotides with Gene-Silencing Applications, B. McGorman et al., 2022, Nucleic Acids Research, Vol. 50(10), p. 5467–5481.
https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkac438
Revolutionizing DNA: advanced modification techniques for next-gen nanotechnology, P. Panda et al., 2024, Nucleosides, Nucleotides & Nucleic Acids, 1–32.
https://doi.org/10.1080/15257770.2024.2432992
Modified Nucleosides, Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids via Click Azide-Alkyne Cycloaddition for Pharmacological Applications, D. Perrone et al., 2021, Molecules, Vol. 26(11), 3100.
https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26113100
FAQ
-
Is C8-Alkyne-dUTP compatible with standard DNA polymerases?
Yes. It is efficiently incorporated by Taq, KOD, Vent, Pwo, and Deep Vent exo- polymerases.
-
What types of molecules can be conjugated post-synthetically?
Azide-functionalized fluorophores, biotin, peptides, sugars, and small molecules.
-
Does the modification affect DNA structure or function?
No. The alkyne group is positioned to preserve DNA integrity and polymerase activity.
-
Can it be used in DNA origami or hydrogel systems?
Yes. It supports spatially controlled modification in nanostructures and hydrogels.
-
Is it suitable for aptamer screening?
Yes. It is used in Click-Particle Display for generating chemically modified aptamers.

