
EdU Cell Proliferation Assay for Imaging
ClickTech EdU Cell Proliferation Kit for Imaging
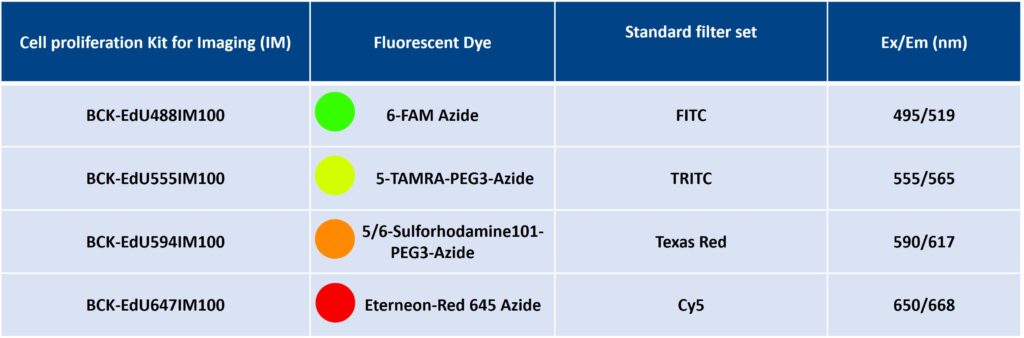
| Size | Catalog No. | Price |
|---|---|---|
| Dye 488 / 100 Assays | BCK-EdU488IM100 | € 495,00 |
| Dye 555 / 100 Assays | BCK-EdU555IM100 | € 495,00 |
| Dye 594 / 100 Assays | BCK-EdU594IM100 | € 495,00 |
| Dye 647 / 100 Assays | BCK-EdU647IM100 | € 495,00 |
Chemical Properties
-
Shelf Life
12 months unopened after receipt
-
Storage Conditions
2-8 °C
-
Physical State
kit system made of different components
-
CAS Number
n.a.
-
Excitation (max)
Dye 488: 496 nm | Dye 555: 546 nm | Dye 594: 584 nm | Dye 647: 643 nm
-
Emission (max)
Dye 488: 516 nm | Dye 555: 579 nm | Dye 594: 603 nm | Dye 647: 662 nm
-
Ɛ (max)
Dye 488: 83.000 cm-1M-1 | Dye 555: 91.000 cm-1M-1 | Dye 594: 110.000 cm-1M-1 | Dye 647: 250.000 cm-1M-1
-
Preparation/Handling
please see user manual of the kit
Product Information
Cell Analysis: Cell Proliferation Imaging Assays
The ClickTech EdU Cell Proliferation Kit for Imaging is a superior alternative to BrdU staining method, for measuring and quantifying de novo DNA synthesis during cell proliferation.
The EdU assay relies on the biorthogonal incorporation of thymidine analog 5-ethynyl-2`-desoxyuridine (5-EdU or EdU) into de novo synthesized DNA. As EdU is not endogenously present in biological molecules, cells, tissues, or model organisms, it can subsequently be conjugated with a bright, photostable dye using click chemistry technology, which was awarded with a Nobel prize in 2022. This reaction is fast, highly specific, and mild, enabling this cell proliferation detection in cancer biology, immunology, cell biology, and developmental biology.
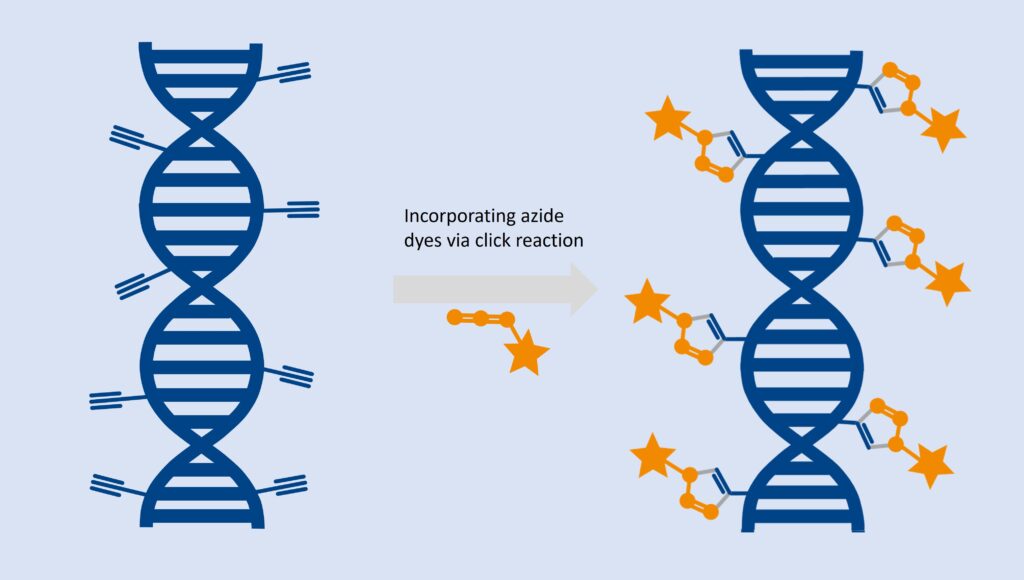
ClickTech EdU Cell Proliferation Kit for Imaging contains chemicals and a protocol optimized for analysis based on fluorescent microscopy applications.
New Feature:
All imaging kits now include DAPI for nuclear counterstaining, enabling simultaneous visualization of DNA synthesis and nuclear morphology. This enhancement supports improved segmentation and staging of replicating cells, especially in imaging-based workflows.
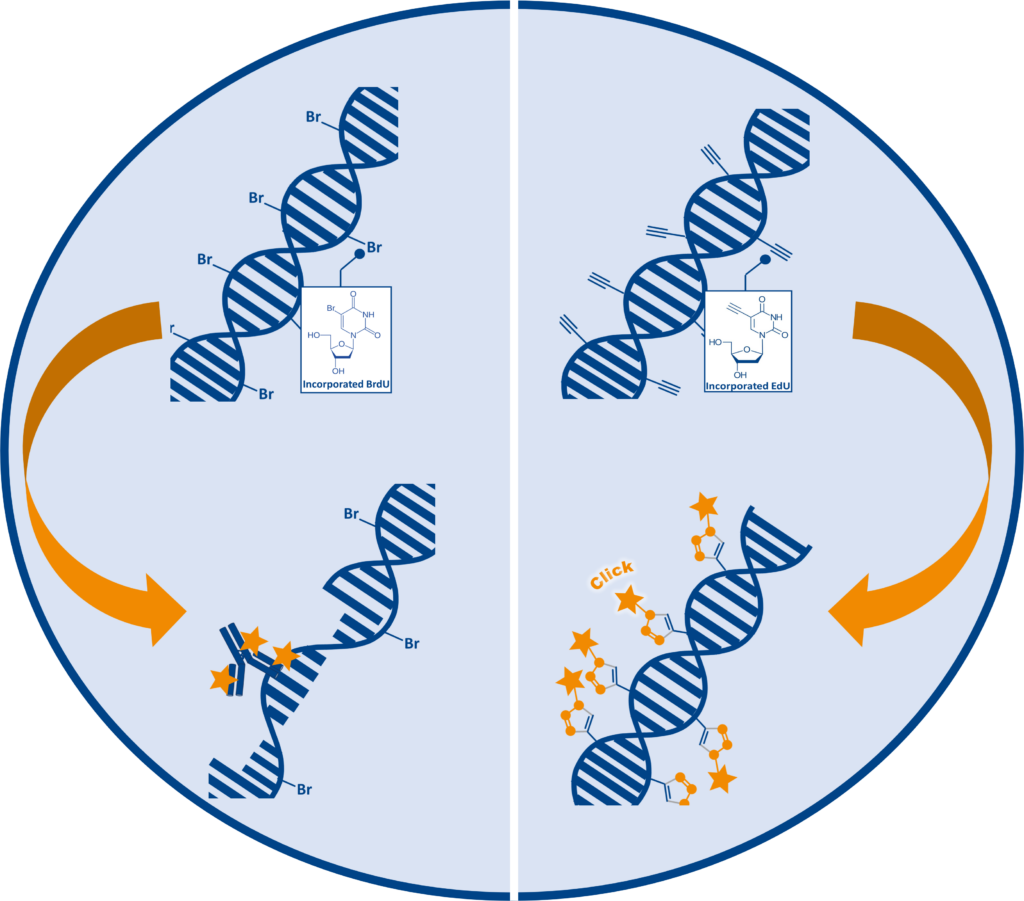
Challenges in traditional cell proliferation assays using 5-Bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU)
Traditional Cell proliferation assays are based on the incorporation of the thymidine analog 5-bromodeoxyuridine (5-BrdU or BrdU) into newly synthesized DNA. BrdU detection depends on anti-BrdU antibodies, which are unable to bind to BrdU within double stranded DNA. Therefore, DNA needs to be denatured to form single stranded DNA (ssDNA) before detection under harsh conditions such as HCl, heat or enzymes. The denaturation step is time consuming and difficult to perform consistently, additionally the necessary harsh treatment can affect sample integrity and quality.
| Category | EdU | BrdU |
| Multiplexing | Compatible with multiple simultaneous labeling | Reduced compatibility epitope damage possible |
| Readout | Fluorescent signal directly indicates sites of DNA replication | Requires DNA denaturation for antibody access |
| Detection | Click Chemistry mediated conjugation | Antibody conjugation |
| DNA Denaturation | None required | Acid treatment / High temperature / Enzyme |
| Antibodies against surface and intracellular markers | Compatible, no structural disruption | Reduced compatibility and epitope damage possible |
| Multiplexing with fluorescent Proteins | No limitation, compatible with standard fluorescent reporters | Imitated fluorescence often affected by processing |
EdU: An enhanced and efficient alternative for cell proliferation assays
The ClickTech EdU cell proliferation assays from baseclick provide an effective solution to the limitations and disadvantages of traditional methods. During the S-Phase of the cell cycle, 5-ethynyl-2′-deoxyuridine (EdU) is incorporated into DNA instead of thymidine during de novo synthesis. Due to the small size of the fluorescent azide, EdU is detected after DNA incorporation without the need for antibodies or DNA denaturation.
Moreover, the reagents provided in ClickTech EdU cell proliferation kits enable mild fixation and permeabilization of cells, allowing sufficient access to DNA for the small molecules used for EdU cell proliferation assays.
The EdU cell proliferation assay is optimized with an easy detection protocol for researchers, simplifying the workflow and the time required. The direct detection procedure for imaging applications is completed within 30 minutes and is compatible with multiplexing for content- and context-rich results.
Reliable and high-resolution cell proliferation analysis with ClickTech EdU Imaging Kit
The ClickTech EdU Imaging Kit provides a fast, consistent, and reliable method to evaluate cell proliferation across various research areas. It supports quantitative, high-resolution detection of replicating cells and is well-suited for imaging-based cell cycle analysis.

Fluorescence imaging of replicating HeLa cells detected with the EdU Cell Proliferation Kit for Imaging (BCK-EdU488IM100). Green signal: EdU labelling; blue signal: DNA counterstaining with DAPI; scale bar = 10 µm. Distinct replication patterns allow staging of replicating cells along S phase (early/mid/late S phase).
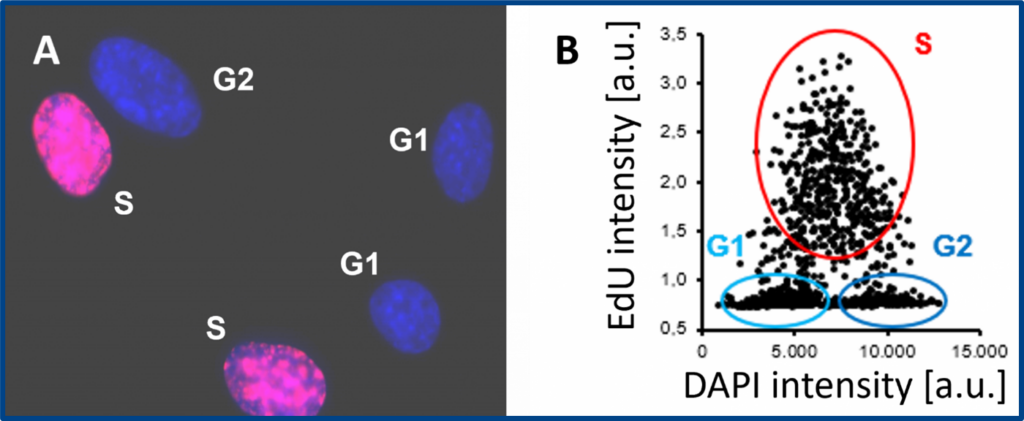
Cell proliferation assay with the EdU Cell Proliferation Kit for Imaging (BCK-EdU647IM100). A) Representative fluorescence microscopy image. Red signal: EdU labelling; blue signal: DNA counterstaining with DAPI. B) Cells in S, G1 and G2/M phases are quantified by image cytometry.
Applications:
- High-resolution analysis of cell proliferation in adherent cultures
- Assessment of drug-induced cell cycle effects in vitro
- Multiplex imaging with nuclear, cytoplasmic, or membrane markers
- Quantitative analysis of S-phase entry in fixed samples
- Research in cancer biology, toxicology, developmental biology, and regenerative medicine
Innovative features of the ClickTech EdU cell proliferation assay for enhanced DNA Synthesis detection
- Enables direct detection of DNA synthesis using EdU incorporation and click chemistry
- Antibody-free protocol ensures low background and preserves cell morphology
- Available in multiple fluorescent dyes for flexible experimental design
- Compatible with adherent cells and multiplex immunostaining workflows
- Simple and fast protocol: complete detection in under 30 minutes
- Now includes DAPI for clear nuclear staining and enhanced cell segmentation
LITERATURE
Anticancer drug and ionizing radiation-induced DNA damage differently influences transcription activity and DDR-related stress responses of an endothelial monolayer, V. Ziegler et al., 2020, Molecular Cell Research, Vol. 1867, p. 118678.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2020.118678
Dendrimer-Based Signal Amplification of Click-Labelled DNA in Situ, N. Raddaoui et al. 2017, ChemBioChem, Vol. 18, p. 1716-1720.
https://doi.org/10.1002/cbic.201700209
High-copy sequences reveal distinct evolution of the rye B chromosome, S. Klemme et al., 2013, New Phytologist, Vol. 199, p. 550-558.
https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.12289
Cytolethal Distending Toxin Promotes Replicative Stress Leading to Genetic Instability Transmitted to Daughter Cells, W. Tremblay et al., 2021, Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology, Vol. 9, 656795.
https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2021.656795
Brassica napus Roots Use Different Strategies to Respond to Warm Temperatures, M. Boter et al., 2023, Int. J. Mol. Sci., Vol. 24(2), 1143.
https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24021143
BMP signaling promotes zebrafish heart regeneration via alleviation of replication stress., M. D. Vasudevarao et al., 2025, Nat Commun, Vol. 16, 1708.
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-56993-6
FAQ
-
What type of cells can incorporate EdU?
The EdU cell proliferation assay has been applied to many different cell types and organisms from prokaryotic to eukaryotic. Cell lines such as E. coli, HeLa, HEK, MOLM are arguably among the most routine applications, but also animals, like mouse, rat, the nematode C. elegans, crickets (Gryllus bimaculatus), chicken (Gallus domesticus) and zebra fish (Danio rerio) or even plants (e.g. Arabidopsis thaliana) can be applied.
Cells that possess a pyrimidine pathway that can phosphorylate EdU to the corresponding triphosphate, which is then accepted by the host DNA polymerase for incorporation into DNA during replication. -
Can I perform EdU cell proliferation detection on living cells?
EdU is incorporated into living cells, but the detection reaction must be performed on fixed and permeabilized samples.
-
How does EdU labeling compare to BrdU or the 3H-thymidine incorporation assay?
All three methods enable to determine cell proliferation directly by incorporation of a metabolite analogue and subsequent detection. The 3H-thymidine incorporation assay is very sensitive, but the radioactive compound requires specialized equipment and dedicated lab space for handling. EdU and BrdU assays are non-radioactive alternatives with decreased risk for health and environment. Compared to the BrdU incorporation assay the EdU assay is more sensitive, requires less handling time and needs no harsh DNA denaturing conditions for detection. Therefore, the EdU cell proliferation is also compatible with multiplexing.
-
Can I combine DAPI staining and EdU detection?
Yes, this is feasible. Please note that DAPI staining should be done after the click detection step. Alternatively, SYBR Green DNA staining can be used. But, please note that SYBR green should not be used with dyes of 488 nm wavelengths.
-
When can I safely interrupt the experiment?
It is possible to safely interrupt the protocol after the fixation step. Thereto, remove the fixation solution and wash as suggested by the user manual, then the cells can be stored in buffer at 4° C. Alternatively, the experiment can also be safely interrupted after permeabilization, again as described above.
Please note: It is important to proceed with the experiment if the click cocktail for the detection of the EdU has been prepared already. -
Is antibody staining compatible with the EdU?
Antibody staining is compatible with EdU cell proliferation detection when antibody detection is done after the click detection step. Please be aware of the dye used for EdU detection. Check also the user manual for more information.
-
How to determine the EdU incubation time?
The EdU incubation time depends on the cell type or organism, the applied EdU concentration and the experimental design. For a start it is advisable to refer to a literature protocol (which is close to your experimental setup) and to test the conditions with a low number of samples. As a general guideline we recommend to use a maximum of 10 µM final EdU in the cell culture medium for incubations. For longer incubation (> 1 day) the concentration should be decreased to 1-5 µM.
-
How does the baseclick ClickTech EdU Cell Proliferation Kit compare to Thermo Fisher’s Click-iT™ EdU Kit?
Our kit is scientifically identical in terms of detection chemistry, both use 5-ethynyl-2′-deoxyuridine (EdU) and click chemistry for DNA synthesis detection. The difference lies in pricing and flexibility, baseclick offers high quality at a significant lower cost.
-
Is there a price advantage over Thermo Fisher’s kit?
Yes. baseclick EdU Cell Proliferation Kits are up to 45% more affordable than Thermo Fisher’s Click-iT™ kits. This cost advantage is especially valuable for high-throughput labs, grant-funded research, and institutions with tight budgets.
-
Do I need to change my protocol if I switch from Thermo Fisher’s kit?
No. Our kits are protocol-compatible with Thermo Fisher’s. You can continue using your existing workflows, instruments, and detection systems without any revalidation or retraining.
-
Is DAPI included in the baseclick EdU Imaging Kits?
Yes. All imaging formats now include DAPI for nuclear counterstaining, enabling simultaneous visualization of DNA synthesis and nuclear morphology.
-
Are bulk discounts available?
Yes. We offer bulk purchasing discounts and long-term supply agreements for academic institutions and research centers. Contact our sales team for a custom quote.

