EdU proliferation: a modern method for analyzing cell growth
The EdU proliferation assay is a sensitive and efficient method for cell proliferation detection and measurement. 5-ethynyl-2′-deoxyuridine (EdU) is a thymidine analogue that incorporates into the newly synthesized DNA of dividing cells during active DNA replication. It can be detected via a copper-catalyzed click chemistry reaction using fluorescent azides. Unlike the traditional BrdU (bromodeoxyuridine) assay, DNA denaturation is not required for the EdU proliferation assay. This preserves cell structure, reduces the harshness for cells and saves assay time.
Understanding edu proliferation in cell biology
EdU structurally mimics thymidine and the cell´s DNA polymerases incorporate it in place of natural thymidine during DNA replication. The EdU contains an ethynyl group that does not interfere with the structure and function of DNA. Following the incorporation of EdU into the de novo synthesized DNA strand, the ethynyl group acts as a chemical partner for azides in the copper-catalysed alkyne azide cycloaddition (CuAAC) click reaction. This reaction enables the sensitive and specific detection of EdU-labelled DNA without denaturing it and providing a direct measurement of cell proliferation.
EdU incorporation specifically marks cells with active DNA synthesis, which occurs in the S-phase of the cell cycle. EdU is then detected using a fluorescent azide label added by a click chemistry reaction, which enables the precise identification and quantification of proliferating cells.
What is an EdU cell proliferation assay?
Principle and mechanism of EdU-based assays
Principle and mechanism of the EdU cell proliferation assay:
- Incorporation: EdU is added to cell cultures or the feed of animals, where it is taken up by proliferating cells. During replication, it partially replaces natural thymidine as nucleobase in DNA.
- Detection (Click Chemistry): as EdU contains an alkyne group it can react with a fluorescently labeled azide in the presence of a copper(I) catalyst (click chemistry (CuAAC) to form a stable triazole linkage.
- Readout: Detection of fluorescently labeled EdU cells using fluorescence microscopy or flow cytometry.
- Learn more about Click Chemistry Glossary here: Click Chemistry Glossary
Advantages:
- No DNA denaturation needed
- High sensitivity and specificity
- Rapid and mild detection processes
EdU cell proliferation assays are highly sensitive, providing precise cell tracking in imaging studies, especially when using enhanced formulations like ClickTech Sensitive EdU Cell Proliferation Kits. This sensitive Edu proliferation assay kit detects EdU at a low concentration of 1–10 µM after short pulse labelling for 15–30 minutes. Improved chemistry, such as the inclusion of copper-chelating azide, enhances detection sensitivity by increasing the local concentration of Cu(I) at the reaction site.
EdU proliferation assays for imaging applications
EdU cell proliferation assays are widely used across various biomedical and life science research fields due to their accuracy, sensitivity, and compatibility with imaging. The detection of EdU-incorporated DNA relies on its reaction with a fluorescent azide to produce a stable, specific fluorescent signal.
EdU cell proliferation assays are compatible with a range of imaging technologies, particularly:
Fluorescence Microscopy: Fluorescence microscopy uses fluorescent dyes that contain an azide moiety to detect cells with EdU-incorporated DNA. After click chemistry (CuAAC) labeling, cells are imaged under a fluorescence microscope using the appropriate filter for the chosen fluorophore (e.g., 488, 555, 594 or 647 dye). Fluorescence microscopy is a simple and fast assay for the basic detection of EdU incorporation.
Confocal Microscopy is used to perform a high-resolution analysis of captured optical sections, enabling 3D imaging of EdU-incorporated cells, tissues or thick samples. Confocal microscopy is ideal for detailed cell cycle analysis and visualizing the co-localization of EdU-positive cells.
Thus, EdU cell proliferation assays provide accurate spatial and temporal analysis of cell proliferation, making them ideal for imaging-based studies in developmental biology, cancer research and tissue regeneration.
- Learn more about EdU assays Glossary here: EdU assays Glossary
Benefits of using EdU cell proliferation assay kits
Among the traditional assays for cell proliferation based on labeled DNA incorporation, EdU proliferation assays offer several significant advantages.
Comprehensive Comparison of Cell Proliferation Assays
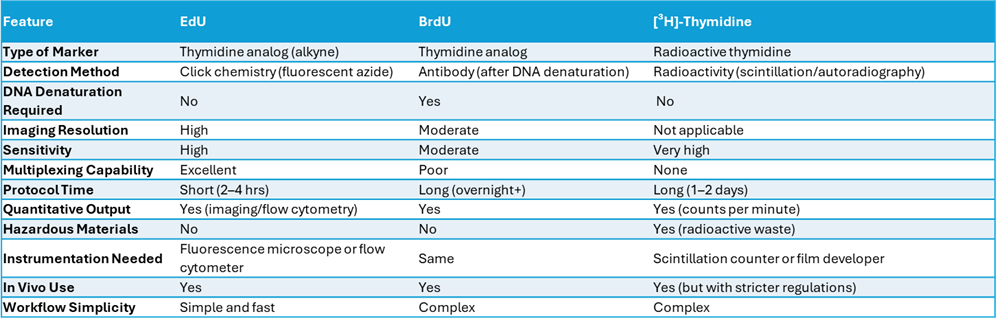
Due to its ability to quickly and precisely detect proliferating cells, EdU cell proliferation assay is particularly useful for imaging studies and identifying dividing cells in complex tissues where accuracy is paramount.
Sensitive and rapid detection of proliferating cells
The sensitive EdU cell proliferation assay, such as the ClickTech Sensitive EdU Cell Proliferation Kit, enables the detection of low levels of DNA synthesis, particularly in low-proliferation samples, by offering EdU detection at non-toxic concentrations of 1–10 µM. The BrdU assay requires higher concentrations (up to 100 µM) than the EdU assay to achieve robust incorporation, due to the antibody’s lower sensitivity and the need for DNA denaturation.
Additionally, the EdU proliferation assay kit provides a significantly faster and simpler protocol than traditional methods such as the BrdU or [³H]-thymidine assays. Unlike the BrdU assay, the EdU assay uses a rapid, highly specific copper-catalyzed click chemistry reaction to detect EdU. This reaction does not require harsh DNA denaturation steps to allow antibody access, thereby reducing total assay time.
The high versatility and compatibility of EdU cell proliferation assays with a wide range of other staining techniques enables detailed, multiparametric analysis. The mild, non-denaturing conditions of EdU detection via a click chemistry reaction preserve cellular and nuclear structures, allowing EdU labeling to be easily combined with other cell staining methods. Immunofluorescence for protein markers, cell cycle analysis (e.g. DAPI or PI staining), apoptosis detection (e.g. TUNEL assay or Annexin V) and differentiation markers are all compatible with EdU assays. This makes EdU assays especially powerful for high-content imaging, tissue analysis and flow cytometry applications, where multiple cellular processes need to be assessed simultaneously.
Flexible assay formats for different platforms
baseclick offers a variety of EdU proliferation assay kits that provide accurate and precise detection of cell proliferation in vitro and in vivo:
- EdU Proliferation Assay Kits for Imaging
- EdU Proliferation Assay Kits for Flow Cytometry
- EdU Proliferation Assay Kits for High-Throughput Screening
Our EdU Proliferation Assay Kits offer a complete, ready-to-use solution for the accurate and efficient analysis of cell proliferation using various detection methods. Each kit includes everything you need: EdU for DNA labeling, a selection of bright fluorescent azide dyes across various spectra, and optimized reagents for fixation, permeabilization, and fast click chemistry–based detection. These kits are built to make your work easier, combining convenience, sensitivity, and flexibility to help you move through your workflow smoothly and get high-quality results.
EdU Proliferation Assay Kits have been developed for specific detection methods and research applications:
- The EdU Proliferation Assay Kits for Imaging is optimized for fluorescence microscopy, providing high-resolution visualization of proliferating cells. They include bright fluorescent azide dyes with a variety of spectra and reagents that are compatible with fixed cells. This allows for clear nuclear labelling via a click chemistry reaction in cell cultures or tissue sections. The kits are ideal for detailed spatial analysis and co-localization studies.
- The EdU Proliferation Assay Kits for Flow Cytometry has been developed for the precise measurement of EdU-incorporated DNA synthesis at the population level, enabling quantitative single-cell analysis. The kit includes optimized reagents for fixation, permeabilization and efficient fluorescent labelling that do not affect cell integrity or scatter properties.
- The EdU Proliferation Assay Kits for High-Throughput Screening has been designed for automated workflows and multi-well plate formats. This kit is optimized for the rapid and reproducible quantification of cell proliferation based on EdU labeling across large sample sets and includes improved reagents for reliable signal intensity and minimal background. The kit is also compatible with robotic liquid handling and fluorescence plate readers. The EdU Proliferation Assay Kit for HTS can be used for drug screening, toxicity testing and compound profiling.
Applications of EdU cell proliferation assays
In biomedical research
Cell proliferation is an important part of the survival strategy of cancer cells and EdU proliferation assays are widely used in cancer research to measure cell proliferation, to track tumor growth and evaluate treatment responses. Specifically, the fluorescent labeling and detection of EdU incorporation into DNA enables the quantification of actively proliferating cells in tumors or cultured cancer cells. For this reason, EdU proliferation assays are valuable tools for estimating tumor aggressiveness and evaluating the effectiveness of anti-cancer treatments aimed at inhibiting proliferation of tumor cells. A decrease in EdU uptake after drug treatment indicates that the drug effectively blocks tumor cell proliferation. EdU proliferation assays provide quantitative with high-resolution insights into tumor biology and treatment effects making them indispensable in both preclinical and clinical cancer research.
The EdU cell proliferation assays are widely used in stem cell biology, particularly for studying cell renewal, differentiation, and tissue regeneration.
Key applications:
- Proliferation tracking for detection of actively dividing stem cells by incorporating EdU during DNA synthesis.
- Assessment of Cell Renewal, namely, the evaluation of the timeframe during which stem cells maintain their undifferentiated state through repeated divisions.
- Tracking Differentiation: The proliferation of stem cells slows down once they have differentiated. Incorporated EdU decreases, indicating a reduction in DNA synthesis and exit from the cell cycle.
- Regeneration Studies: EdU is used to detect and track stem cell activation after injury and during the repair process in regenerative experiments.
In pharmaceutical and toxicology studies
EdU proliferation assays are a highly sensitive, fast and reliable tool for evaluating the effect of compounds on cell division in drug screening. EdU incorporation into DNA during the S-phase serves as a direct marker of proliferating cells.
Role of EdU Assays in Drug Screening:
- Measuring drug impact on cell proliferation
- Compatibility with automated imaging and flow cytometry enables the rapid testing of many compounds and fast identification drugs that suppress or stimulate proliferation.
- A combination of EdU proliferation assays with other markers (e.g. apoptosis or cell cycle proteins) enables the identification of the mechanism of drug action.
In summary, EdU proliferation assays are fast and sensitive and applicable to a wide range of cell types, making them essential for drug screening.
The EdU proliferation assays are widely used in toxicology to assess the effects of chemicals on cell proliferation, a critical indicator of cellular health and function.
Key applications:
- Cytotoxicity Screening
- Dose-Response Testing
- Cell-Type Sensitivity.
- Pathway Analysis.
EdU proliferation assays are ideal for chemical safety testing and regulatory studies due to their sensitivity, scalability and simplicity and speed of performance.
Choosing the right EdU proliferation assay kit
Choosing the right EdU proliferation assay kit depends on experimental goals and detection method.
- The EdU Proliferation Assay Kits for Imaging are ideal for visualizing proliferating cells in fixed samples, such as tissue sections or cultured cells. The kits include fluorescent dye-conjugated azides, such as 6-FAM (488 nm), 5-TAMRA-PEG3 (555 nm), 5/6-Sulforodamine 101-PEG3 (594 nm) and Eterneon-Red 645 (647 nm), and all are compatible with immunofluorescence and co-staining.
- The EdU Proliferation Assay Kits for Flow Cytometry are ideal for quantifying proliferation in large cell populations. Protocols for cell fixation and permeabilization as well as fluorescent azides have been optimized for flow cytometry.
- The EdU Proliferation Assay Kits for High-Throughput Screening are ideal for testing many compounds in 96-well plates and optimized for use with plate readers or automated imaging. The kits provide robust signals and a low background. ClickTech EdU HTS Kits offer fluorescent 6-FAM- azides (488 nm) and 5-TAMRA-PEG3-azide (555 nm).
Pick based on your detection method, sample type, and experimental scale.

