
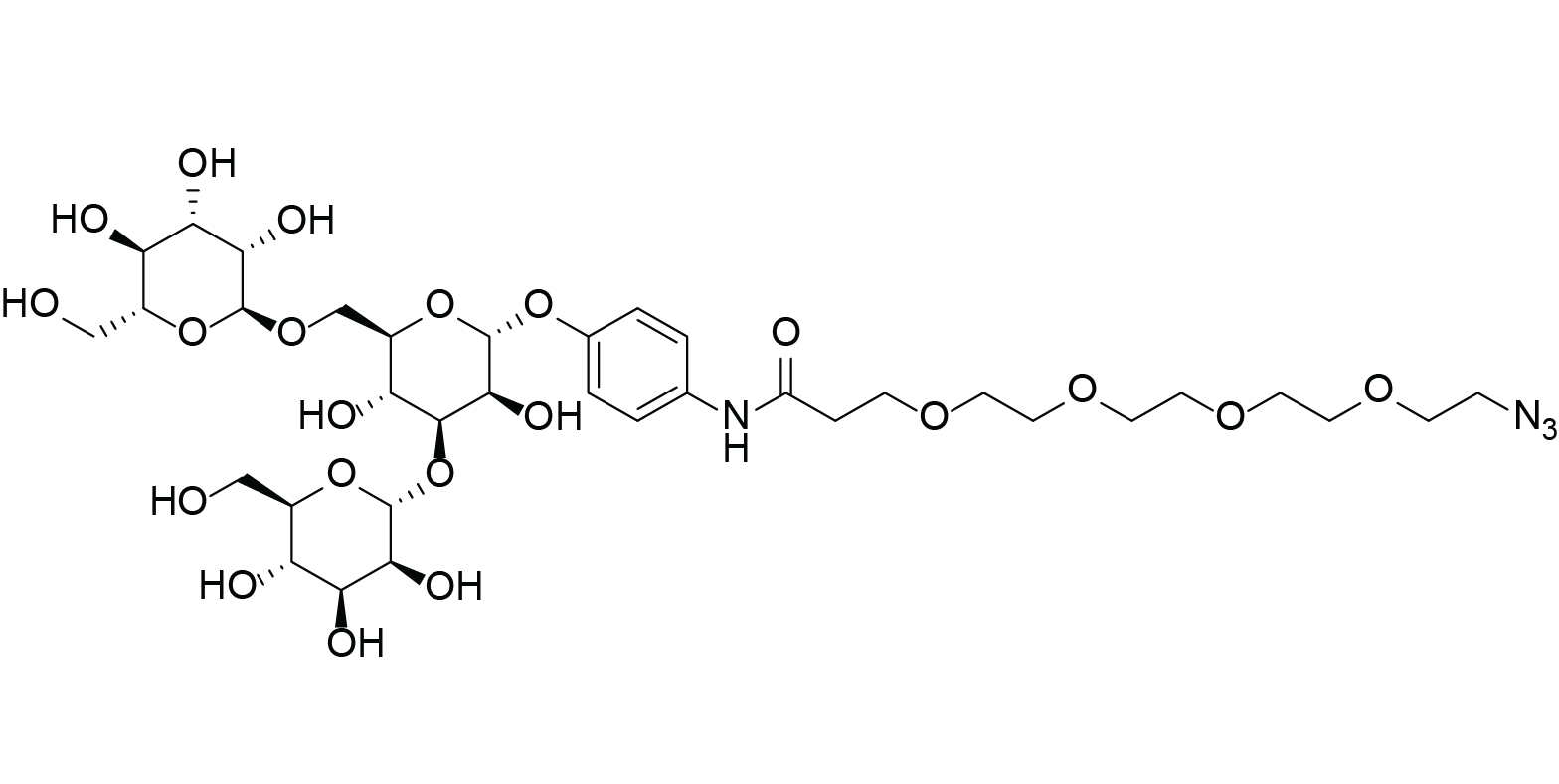
Azido-PEG4-Trimannose
Clickable trimannose identifier for target delivery
| Size | Catalog No. | Price |
|---|---|---|
| 5 mg | BCFA-244-5 | € 400,00 |
| 10 mg | BCFA-244-10 | € 680,00 |
Chemical Properties
-
Molecular Formula
C35H56N4O21
-
Shelf Life
12 months unopened after receipt
-
Storage Conditions
-20 °C, dark, inert gas
-
Molecular Weight
868.83 g/mol
-
Purity
≥ 98% (HPLC)
-
Physical State
white amorphous solid
-
CAS Number
n.a.
-
Additional name
Azido-PEG4-carbonylaminophenyl 3,6-di-O-(α-D-mannopyranosyl)-α-D-mannopyranoside
-
Solubility
H2O, DMSO
-
Preparation/Handling
For a 10 mM solution add 575 μL to 5 mg.
For a 10 mM solution add 1151 μL to 10 mg.
Product Information
A Bioorthogonal Linker for Targeted Glycoconjugation
Azido-PEG4-Trimannose is a PEG derivative composed of an azido (-N3) group, a PEG4 spacer, and a trimannose saccharide moiety (3,6‑di‑O‑(α-D-mannopyranosyl)-α-D-mannopyranoside). The azido group allows bioorthogonal conjugation via click chemistry, the PEG4 linker enhances solubility and structural flexibility, and the trimannose moiety facilitates lectin binding for receptor recognition. This design ensures efficient bioconjugation, stability in aqueous environments, and selective molecular interactions.
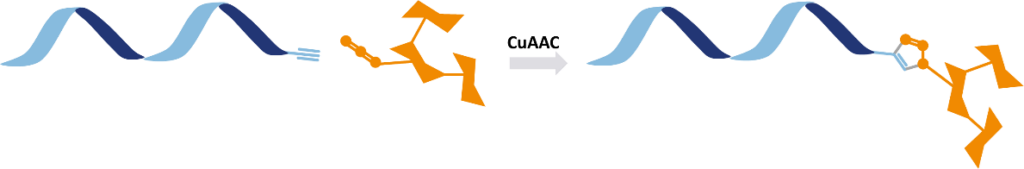
Production and delivery of biological molecules for research purposes and drug development face key challenges as: low specificity, weak receptor binding, unstable conjugation, poor cellular uptake and steric hindrance leading to aggregation. Existing methods lacked efficiency, reducing therapeutic impact and limiting controlled biomolecule ligand conjugation.
How Azido‑PEG4‑Trimannose overcomes Bioconjugation challenges
Azido-PEG4-Trimannose addresses these issues by employing key structural advantages:
- PEG4 Spacer for Solubility & Flexibility: Enhances water solubility, reducing aggregation and maintaining biomolecule functionality.
- Optimized Targeting with Trimannose: Recognized by mannose receptors, ensuring specific uptake by mannose receptor expressing cells such as macrophages or dendritic cells.
- Multivalent Binding for Enhanced Affinity: Forms a trivalent cluster, mimicking the N-glycan core for stronger Concovalin A (Con A) interactions.
- Highly Efficient Bioconjugation: The azido (-N3) group enables CuAAC and SPAAC click chemistry conjugation, ensuring stable, high-yield, orthogonal and pure attachment to biomolecules.
- Steric Hindrance Reduction: The elongated PEG4 linker minimizes steric clashes, ensuring receptor accessibility and efficient endocytosis.
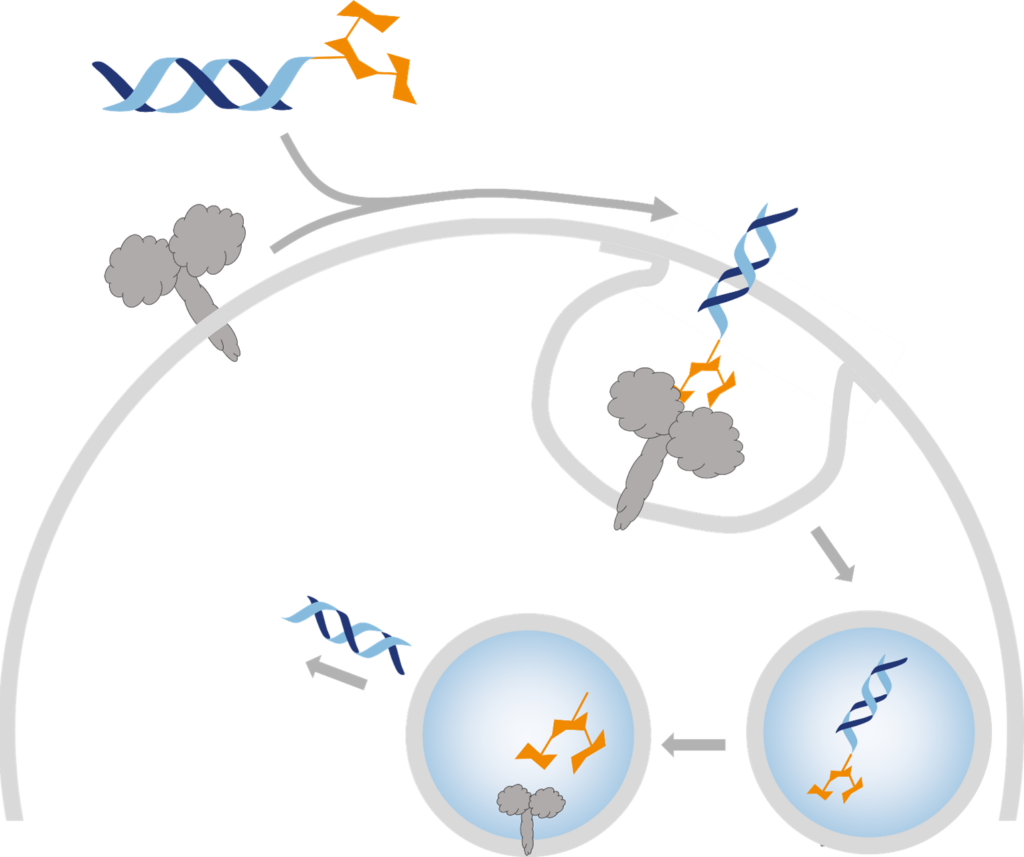
Applications in Research and Industry
Azido-PEG4-Trimannose plays a critical role in various biomedical and therapeutic applications:
- Targeted Drug Delivery: Used in inhaled oligonucleotide formulations, directing drugs to pulmonary macrophages to reduce lung inflammation.
- Immunotherapy & Vaccine Development: Functionalized nanogels and liposomes improve antigen uptake in dendritic cells.
- Bioconjugation in Research: Applied in glycobiology studies to analyze mannose receptor interactions.
- Surface Modifications: Ensures precise functionalization of proteins, liposomes, and nanoparticles in biomedical engineering.
Azido-PEG4-Trimannose is a game-changer in bioconjugation and targeted drug delivery, effectively resolving prior challenges related to binding affinity, steric hindrance, solubility, and receptor-mediated uptake. By integrating the PEG4 linker, it enhances drug delivery precision, stability, and therapeutic efficiency. Its broad applications in immunotherapy, molecular research, and nanomedicine solidify its importance in advancing biomedical engineering.
LITERATURE
Synthesis and affinities of C3-symmetric thioglycoside-containing trimannosides, J. Bi et al., 2015, Carbohydrate Research, Vol. 412, p. 56-65.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carres.2015.05.001
A structure of the complex between concanavalin A and methyl-3, 6-di-O-(α-D-mannopyranosyl)-α-D-mannopyranoside reveals two binding modes, R. Loris et al., 1996, Journal of Biological Chemistry, Vol. 271(48), p. 30614-30618.
https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.271.48.30614
Trimannose-coupled antimiR-21 for macrophage-targeted inhalation treatment of acute inflammatory lung damage, Christina Beck et al., 2023, Nature Communications, Vol. 14, Article number: 4564 (2023)

