
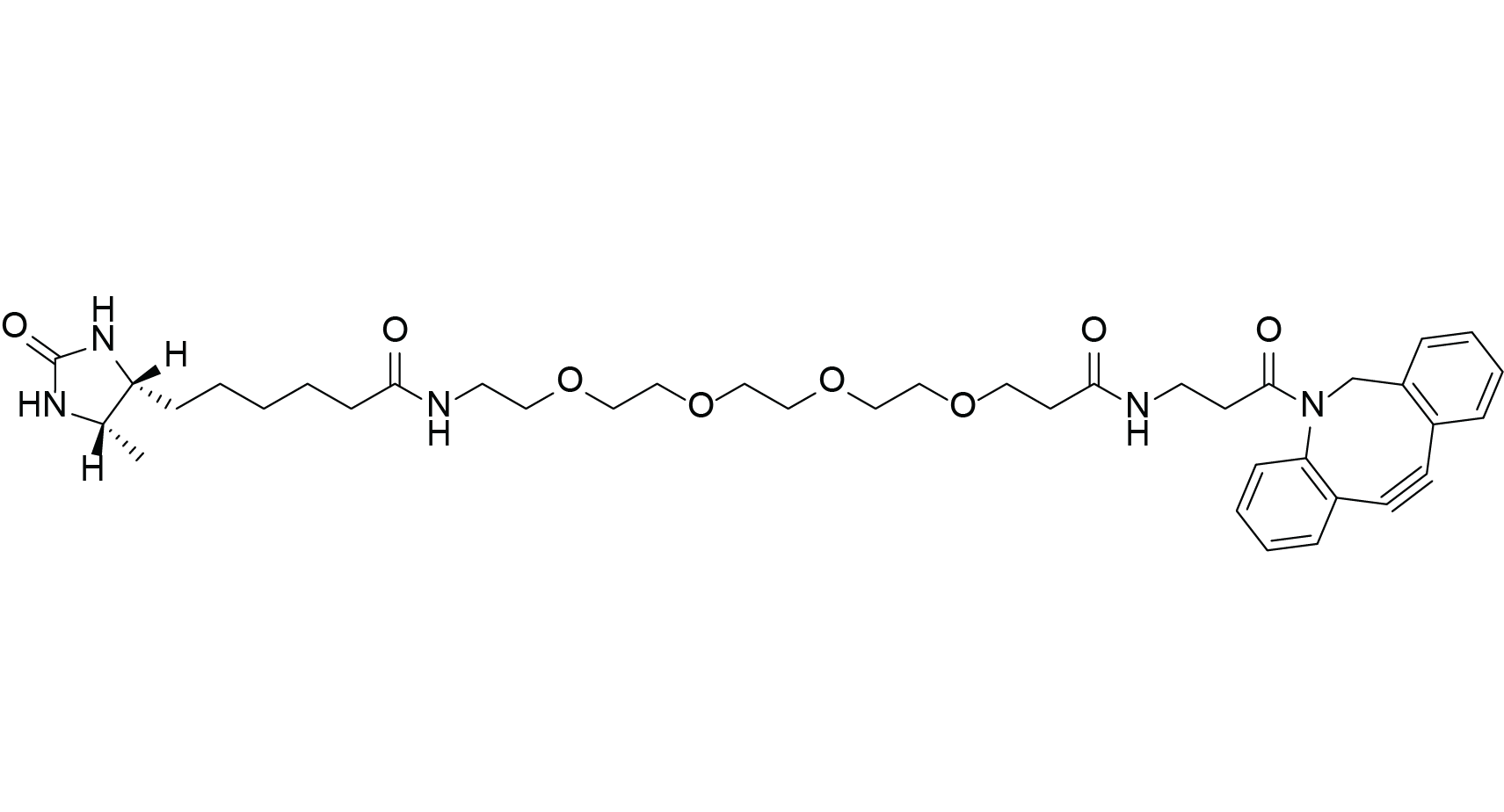
DBCO-PEG4-Desthiobiotin
Desthiobiotinylation reagent for labeling by SPAAC
| Size | Catalog No. | Price |
|---|---|---|
| 5 mg | BCFA-233-5 | € 140,00 |
Chemical Properties
-
Molecular Formula
C39H53N5O8
-
Shelf Life
12 months unopened after receipt
-
Storage Conditions
-20 °C, dark, inert gas
-
Molecular Weight
719.87 g/mol
-
Purity
≥ 95% (HPLC)
-
Physical State
colorless to slightly yellow oil
-
CAS Number
2032788-37-5
-
Solubility
DMSO, DMF, MeOH, DCM, THF
-
Preparation/Handling
For a 10 mM solution add 695 μL to 5 mg.
For a 10 mM solution add 1389 μL to 10 mg.
Product Information
A desthio-biotinylation reagent for labeling of azido modified targets by strain-promoted azide alkyne cycloaddition (SPAAC)
What is Desthiobiotin
Desthiobiotin is a sulfur free analog to biotin through which it only consists out of a single heterocycle. It is known to bind with similar specificity but less affinity as biotin (Kd = 1011 vs. 1015 M) to the protein streptavidin. This bonding is utilized in many research fields in modern biochemistry such as peptide/protein and nucleic acid research since this behavior can be utilized to specific binding of desthiobiotin labeled targets to streptavidin and subsequent mild release by free biotin. The same binding effect is also occurring for avidin.
Applications of Desthiobiotin
Desthibiotin is most used in biotechnology for purification and enrichment workflows. These typically involve chemical labeling of target molecules with desthiobiotin, followed by capture using streptavidin-coated magnetic beads or resins. Non-labeled impurities are removed during washing steps.
Release of purified molecules is achieved by elution with a biotin-containing buffer, which selectively displaces desthiobiotin-labeled molecules while leaving biotin-labeled species bound.
Key advantages:
- Mild release conditions preserve native structures and functionality, even for active proteins.
- Unlike biotin, which forms an irreversible complex with streptavidin, desthiobiotin allows reversible binding without harsh denaturing conditions or cleavable linkers.
Beyond purification, this approach is also used for identifying RNA-binding proteins under native conditions: RNA is labeled with desthiobiotin, purified, and then released with biotin. Proteins co-purified in this process are confirmed RNA-binding candidates.
To enable these techniques, desthiobiotin-labeled biomolecules are required. Click chemistry offers a simple and cost-effective method for generating such molecules. This requires biomolecules modified with azide or alkyne groups. Both modified biomolecules and reagents like DBCO-PEG4-Desthiobiotin are commercially available.
For azide/alkyne-modified or pre-labeled Oligos/mRNA, baseclick provides direct solutions. For other targets, please contact us at support@baseclick.eu to discuss feasibility.
Chemical Properties of DBCO-PEG4-Desthiobiotin
DBCO-PEG4-Desthiobiotin enables desthiobiotin labeling under very mild conditions using SPAAC click chemistry. Unlike CuAAC, SPAAC requires no heating or catalyst, forming stable triazole linkages with azides, ideal for in vivo labeling.
Additional features:
- Bioorthogonal reaction: Does not interfere with biological functions.
- PEG4 spacer: Improves water solubility and reduces steric hindrance between desthiobiotin and the target molecule.
These properties make DBCO-PEG4-Desthiobiotin the optimal choice for labeling azide-modified biomolecules such as peptides, proteins, and nucleic acids, especially when copper-free conditions are required. Moreover, click chemistry allows precise control over labeling positions, unlike traditional NHS ester chemistry.
LITERATURE
Quantitative secretome analysis of activated Jurkat cells using click chemistry-based enrichment of secreted glycoproteins, K. E. Witzke et al., 2017, Journal of Proteome Research, Vol. 16(1), p. 137-146.
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jproteome.6b00575
Tetracyclines modify translation by targeting key human rRNA substructures, J. D. Mortison et al., 2018, Cell chemical biology, Vol. 25(12), p. 1506-1518.

