
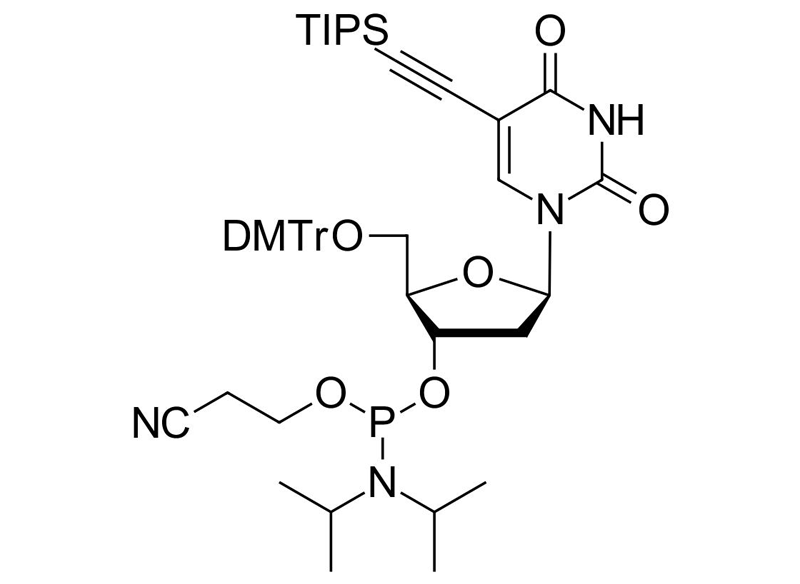
TIPS-5-Ethynyl-dU-CE Phosphoramidite
Clickable phosphoramidite for Oligo synthesis
| Size | Catalog No. | Price |
|---|---|---|
| 100 mg | BCA-25-100 | € 250,00 |
| 250 mg | BCA-25-250 | € 580,00 |
| 1 g | BCA-25-1g | € 1.800,00 |
Chemical Properties
-
Molecular Formula
C50H67N4O8PSi
-
Shelf Life
12 months unopened after receipt
-
Storage Conditions
-20 °C dry, inert gas
-
Molecular Weight
911.16 g/mol
-
Purity
≥ 95% (HPLC and 31P NMR)
-
Physical State
off-white colored fluffy solid
-
CAS Number
1472616-97-9
-
Additional name
5-TIPS-EDU Amidite; TIPS-5-Ethynyl dU CEP; TIPS-5-Ethynyl dU Phosphoramidite
Product Information
Advanced Building Block for Click-Enabled Oligonucleotide
TIPS-5-Ethynyl-dU-CE Phosphoramidite is a specialized reagent for solid-phase oligonucleotide synthesis, featuring a triisopropylsilyl (TIPS) protecting group on the ethynyl functionality. This design prevents base-catalyzed hydrolization, ensuring high stability, purity, and efficiency in DNA and RNA modifications. It is ideal for click chemistry conjugation via Copper(I)-Catalyzed Azide-Alkyne Cycloaddition (CuAAC), enabling site-specific labeling, bioconjugation, and fluorescent dye incorporation.
Challenges Before TIPS-Protection
Researchers previously faced:
Base-Catalyzed Hydration: Ethynyl groups in standard 5-Ethynyl-dU phosphoramidites were prone to hydration under strong base or heat, forming methyl ketones unsuitable for click reactions.
Side Product Formation: Conventional synthesis yielded low purity and unwanted modifications.
Limited Sequential Click Modifications: Multi-step conjugation was difficult due to lack of controlled protection strategies.
Why TIPS Protection Matters
- Hydration Prevention: Shields the ethynyl group from base/acid-catalyzed side reactions.
- High-Purity Oligos: Achieve >10 modifications with excellent yield and chemical integrity.
- Sequential Click Chemistry: Perform dual or multi-step conjugations—click first on an unprotected alkyne (e.g., C8-Alkyne-dU-CE), then deprotect TIPS for a second click.
- Improved RP-HPLC Purification: Hydrophobic TIPS group enhances retention and peak resolution, simplifying separation from n-1 impurities.
Dual-Click Strategy
Combine TIPS-5-Ethynyl-dU-CEP with for example C8-Alkyne-dU-CE Phosphoramidite in the same oligo to create two independent clickable sites:
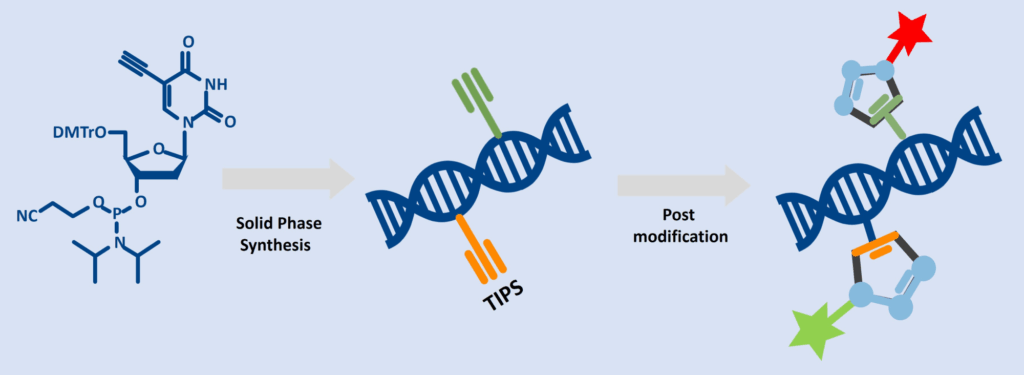
This workflow demonstrates how multi-click chemistry enables two independent labeling steps on the same DNA strand:
- Solid-Phase Synthesis
The oligonucleotide is assembled with two clickable building blocks:
- C8-Alkyne-dU (unprotected)
- TIPS-5-Ethynyl-dU (protected ethynyl group)
- Post modification
The unprotected alkyne is clicked with an azide-functionalized dye or biomolecule using CuAAC, introducing the first label without affecting the TIPS-protected site.
After the first click, the TIPS group is removed, deprotecting the second ethynyl functionality. A subsequent second click reaction adds another label, enabling dual-color imaging, multi-functional probes, or complex bioconjugates.
This approach enables multi-functional oligonucleotides for advanced applications in:
- Diagnostics (dual-color probes)
- Therapeutics (drug-oligo conjugates)
- Molecular imaging (multi-fluorophore labeling)
- Nanotechnology (multi-ligand interfaces)
Comparison between protected and unprotected dU-CE Phosphoramidite
| Feature | TIPS-5-Ethynyl-dU-CE Phosphoramidite | 5-Ethynyl-dU-CE Phosphoramidite |
| Protecting Group | Triisopropylsilyl (TIPS) | None |
| Purpose of Protection | Prevents base-catalyzed hydration of ethynyl group during synthesis and workup | Ethynyl group is unprotected, prone to hydration and side reactions |
| Side Product Risk | Minimal — TIPS protection avoids acetyl derivative formation | Higher — hydrolysation can lead to methyl ketone or acetyl derivatives |
| Sequential Click Chemistry | Yes — first click on unprotected alkyne, then TIPS deprotection for second click | No — only single click modification possible |
| Purification Advantage | Better RP-HPLC resolution due to hydrophobic TIPS group (sharper peaks, easier separation from n-1 impurities) | Standard RP-HPLC, less retention difference |
| Applications | Complex oligos with multiple clickable sites; dual labeling strategies | Standard clickable oligos for single modification |
| Price | ~€250 (100 mg), €580 (250 mg), €1,800 (1 g) | ~€320 (250 mg), €1,050 (1 g) |
| CAS Number | 1472616-97-9 | 615288-66-9 |
| Purity | ≥ 95% (HPLC & 31P NMR) | ≥ 95% (HPLC & 31P NMR) |
| Storage | −20 °C, dry, inert gas | −20 °C, dry, inert gas |
Applications
- Diagnostic assays
- Therapeutic oligonucleotides
- Molecular imaging
- Multi-functional nucleic acid conjugates
Complementary Products
LITERATURE
Ethynyl Side Chain Hydration during Synthesis and Workup of “Clickable” Oligonucleotides: Bypassing Acetyl Group Formation by Triisopropylsilyl Protection, S. A. Ingale et al., 2013, J. Org. Chem., Vol. 78, p. 11271–11282.
https://doi.org/10.1021/jo401780u
Nucleosides And Oligonucleotides With Diynyl Side Chains: The Huisgen-Sharpless Cycloaddition “Click Reaction” Performed On Dna And Their Constituents, F. Seela et al., 2007, Nucleosides, Nucleotides & Nucleic Acids, Vol. 26, p. 597–601.
https://doi.org/10.1080/15257770701490308
Postsynthetic DNA Modification through the Copper-Catalyzed Azide–Alkyne Cycloaddition Reaction, P. M. E. Gramlich et al., 2008, Angew. Chemie Int. Ed., Vol. 47, p. 8350–8358.
https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200802077
Efficiency and Fidelity in a Click-Chemistry Route to Triazole Dendrimers by the Copper(I)-Catalyzed Ligation of Azides and Alkynes, P. Wu et al., 2004, Angew. Chemie Int. Ed., Vol. 43, p. 3928–3932.
https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200454078
Peptidotriazoles on Solid Phase: [1,2,3]-Triazoles by Regiospecific Copper(I)-Catalyzed 1,3-Dipolar Cycloadditions of Terminal Alkynes to Azides, C. W. Tornøe et al., 2002, J. Org. Chem., Vol. 67, p. 3057–3064.
https://doi.org/10.1021/jo011148j
Click Chemistry: Diverse Chemical Function from a Few Good Reactions, H. C. Kolb et al., 2001, Angew. Chemie Int. Ed., Vol. 40, p. 2004–2021.
https://doi.org/10.1002/1521-3773(20010601)40:11<2004::AID-ANIE2004>3.0.CO;2-5
FAQ
-
Why use TIPS-5-Ethynyl-dU-CEP instead of standard 5-Ethynyl-dU-CEP?
Because the TIPS protecting group prevents base-catalyzed hydration and side reactions, ensuring higher stability, purity, and enabling multi-step click chemistry.
-
Can I perform dual or multi-click labeling with this phosphoramidite?
Yes. After synthesis, you can: Click on an unprotected alkyne (e.g., C8-Alkyne-dU), Remove TIPS under mild conditions, Perform a second click on the exposed ethynyl group.
-
How does TIPS protection improve RP-HPLC purification?
The hydrophobic TIPS group enhances retention and peak resolution, making it easier to separate the desired product from n-1 impurities.
-
Is TIPS removal complicated?
No. It can be removed under mild conditions without damaging the oligo, enabling the second click reaction.
-
Is it compatible with standard oligo synthesis protocols?
Yes. It integrates seamlessly into conventional phosphoramidite workflows.
-
What storage conditions are recommended?
Store at −20 °C, dry, under inert gas. Avoid moisture and repeated freeze-thaw cycles.

