
Uridine 5′-triphosphate (UTP)
Triphosphate for RNA synthesis and transcription
| Size | Catalog No. | Price |
|---|---|---|
| 1 ml | BCT-45-S | € 60,00 |
| 10 ml | BCT-45-L | € 360,00 |
Chemical Properties
-
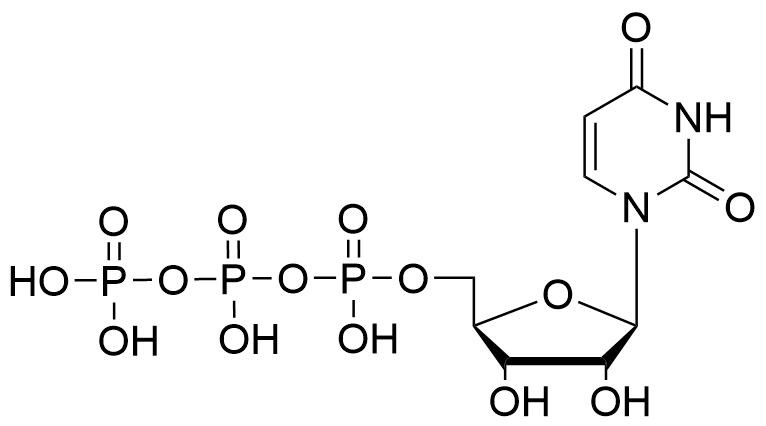
Molecular Formula
C9H15N2O15P3
-
Shelf Life
12 months unopened after receipt
-
Storage Conditions
-20 °C
-
Molecular Weight
488.14 g/mol
-
Purity
≥ 98.5% (HPLC), pH 8.3 ± 0.2
-
Physical State
100 mM solution in water
-
CAS Number
63-39-8 (free acid), 19817-92-6 (trisodium salt)
-
Absorption (max)
λmax = 260 nm
-
Ɛ (max)
15,000 cm-1M-1 (pH 7.0)
Product Information
Essential Nucleotide for RNA Synthesis and Cellular Metabolism
Uridine 5′-triphosphate (UTP) is a vital ribonucleoside triphosphate composed of uridine and three phosphate groups. As one of the four primary building blocks of RNA (alongside ATP, GTP, and CTP), UTP plays a central role in RNA transcription, glycosylation, energy transfer, and cell signaling.
Key Functions & Applications
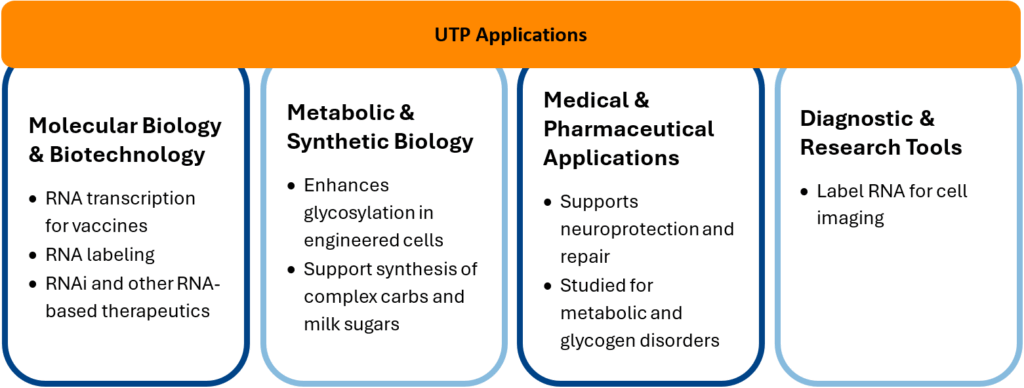
- RNA Synthesis: UTP provides uridine monophosphate (UMP) units during transcription, enabling both natural and synthetic RNA production.
- Glycosylation & Sugar Activation: UTP forms UDP-sugars (e.g., UDP-glucose, UDP-galactose), which are essential for glycogen biosynthesis and protein/lipid glycosylation.
- Energy Transfer: In specific metabolic reactions, UTP substitutes for ATP, acting as an energy donor—notably in the conversion of glucose-1-phosphate to UDP-glucose.
- Signal Transduction: UTP activates P2Y2 receptors, influencing vasodilation, ion transport, and immune response regulation.
UTP now plays a pivotal role across several research and clinical domains:
Scientific Impact
The discovery and characterization of UTP revolutionized molecular biology by:
- Clarifying the role of uridine in RNA synthesis
- Enabling controlled RNA production in laboratory settings
- Expanding understanding of nucleotide-based signaling pathways
- Supporting innovations in diagnostics, therapeutics, and synthetic biology
FAQ
-
What is UTP used for in molecular biology?
UTP is used as a substrate for RNA polymerases during RNA synthesis and as a precursor for UDP-sugars in glycosylation pathways.
-
How does UTP contribute to energy metabolism?
UTP can act as an alternative energy donor to ATP in certain reactions, such as the formation of UDP-glucose during glycogen biosynthesis.
-
What role does UTP play in cell signaling?
UTP activates P2Y2 receptors, which are involved in cellular communication, vasodilation, and immune regulation.
-
Is UTP involved in glycosylation?
Yes. UTP forms UDP-sugars, which are critical intermediates in the glycosylation of proteins and lipids.
-
Can UTP be used in RNA synthesis in vitro?
Absolutely. UTP is a standard reagent in in vitro transcription kits and RNA synthesis protocols.
-
What distinguishes UTP from other nucleotides like ATP or GTP?
While ATP and GTP are also energy carriers and RNA building blocks, UTP is uniquely involved in glycosylation and uridine-based signaling.
-
Is UTP stable under standard lab conditions?
Yes. UTP is typically supplied as a sodium salt and remains stable under neutral pH and cold storage conditions.
-
What are UDP-sugars and why are they important?
UDP-sugars are activated sugar molecules derived from UTP, essential for biosynthetic pathways like glycogen formation and glycoprotein assembly.
-
How is UTP stored and handled in the lab?
UTP should be stored at –20°C, protected from moisture and repeated freeze-thaw cycles to maintain stability.
-
Where can I purchase UTP for research use?
UTP is available through baseclick’s webshop and authorized distributors. Contact baseclick for bulk quantities or technical support.

