
Biotin Azide Plus
Improved biotinylation reagent for labeling by CuAAC
| Size | Catalog No. | Price |
|---|---|---|
| 5 mg | BCFA-235-5 | € 290,00 |
Chemical Properties
-
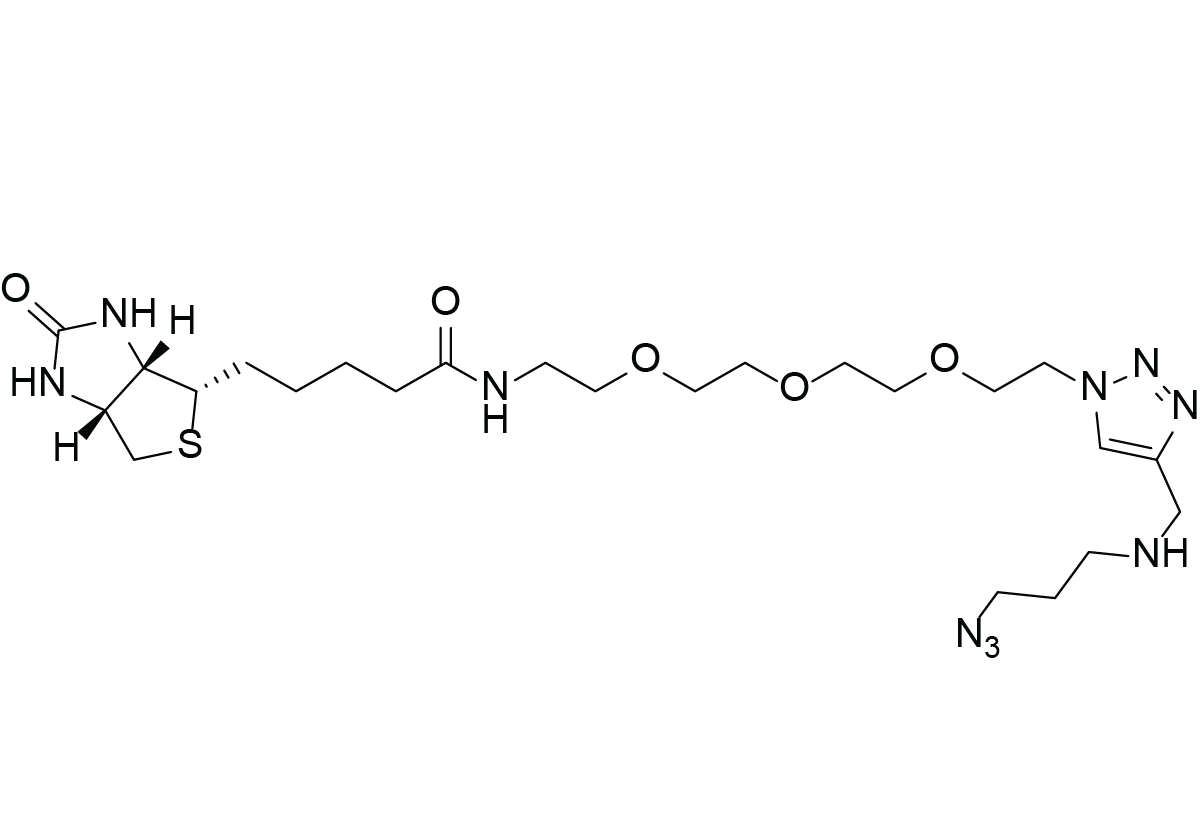
Molecular Formula
C24H42N10O5S
-
Shelf Life
12 months unopened after receipt
-
Storage Conditions
-20 °C, dark, inert gas
-
Molecular Weight
582.72 g/mol
-
Purity
≥ 95% (HPLC)
-
Physical State
off-white to slightly orange amorphous solid or oil
-
CAS Number
n.a.
-
Solubility
DMSO, DMF, MeOH
-
Preparation/Handling
For a 10 mM solution add 858 μL to 5 mg.
For a 10 mM solution add 1716 μL to 10 mg.
Product Information
A biotin labeling reagent for biomolecules using copper catalyzed azide alkyne cycloaddition (CuAAC) with minimal copper concentrations
What is biotin
Biotin, also known as vitamin B7, is a sulfur and nitrogen containing bi-heterocyclus which is used as coenzyme in metabolism. Biotin is used as coenzyme for carboxylation enzymes such as Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase or Pyruvate Carboxylase. Next to its function as coenzym, biotin is known to undergo one of the strongest non-covalent bonds known today to the proteins avidin and streptavidin. The formation of this strong complex is utilized in many research fields in modern biochemistry such as in peptide/protein and nucleic acid research. Usually, streptavidin is used because it is better soluble at neutral pH and has less unspecific binding than avidin.
Applications of biotin
Peptide/protein research:
The biotin streptavidin complex is used for many applications in research. Biotinylation of peptides is widely used for affinity purification. Binding of the biotin marked proteins or complexes to magnetic beads or columns allows for a simple one-step purification. Additionally, it enables the detection of biotin labelled targets by conjugation with streptavidin conjugated reporters. As reporters mostly fluorophores or enzymes as horseradish peroxidase (HRP) are used. Biotinylation is often used in immunoassays such as ELISA, Western Blot or Immunohistochemistry. It also enables the enrichment of certain proteins as exemplary newly synthesized ones for mass spectroscopy analysis. Fixation of biotin tagged proteins on a Streptavidin coated surface allows performing binding assays to study protein interactions.
Nucleic acid research:
In nucleic acid research biotin labeling is mostly used for purification processes. Again, the biotin bonding to Streptavidin containing beads, columns or resins is utilized to link the nucleic acids to the solid support and separate them from impurities. Biotin containing probes can be used in in situ hybridization (ISH), Southern blots or Northern blots for binding to specific DNA/RNA structures. The probes can be visualized and localized afterwards by binding to Streptavidin based markers which again carry usually a dye or an enzyme for detection.
For all these techniques biotin labeled biomolecules are needed. A cheap and easy to perform technique to produce these, is click chemistry. For using click chemistry a modified biomolecule is needed carrying a terminal alkyne. Biomolecules carrying this modification are usually available for purchase. Biotin labelled Oligos/mRNA are directly available from baseclick as well as modified nucleic acids containing terminal alkynes for custom labeling. For other targets please contact us via support@baseclick.eu if you have any questions.
Chemical Properties of Biotin Azide Plus
Biotin Azide Plus is a chemical for biotin labeling under the mild conditions of copper catalyzed azide alkyne cycloadditon (CuAAC) click chemistry. The azide plus linker is specifically designed to enable click chemistry with reduced copper concentration. If the copper free strain promoted alternative should be used, the azide plus linker is not providing any advantage and e.g. Biotin-PEG4-Azide is a cost effective alternative.
Click chemistry is considered to be bioothogonal, meaning that the functional groups included in the reaction do not interfere with any of the functionalities of living organisms. Additionally, the azide plus moiety is able to chelate copper ions, increasing reaction speed by providing the catalyst while providing protection to copper ions for them to catalyze side reactions. This is possible due to the fact that the azide plus functionality is chelating copper. This allows also to reduce the copper concentration during the reaction while maintaining the same results without the need to mandatory use a copper chelating ligand as THPTA.
These chemical properties make Biotin Azide Plus the ideal choice for biotin labeling of all kinds of terminal alkyne modified sensitive biomolecules such as peptides/proteins and nucleic acids if the strain promoted variant should be circumvented. The strain promoted alkyne azide cycloaddition (SPAAC) has some disadvantages as producing two isomers or the need for bulky strained alkynes as DBCO groups.
Since Click Chemistry utilizes non-natural occurring modifications, the possible positions of biotin labeling can be strongly controlled unlike traditional biotin labeling processes as NHS ester chemistry.
LITERATURE
Essential requirement for JPT2 in NAADP-evoked Ca2+ signaling, G. S. Gunaratne et al., 2021, Science Signaling, Vol. 14(675), eabd5605.
https://doi.org/10.1126/scisignal.abd5605
TMEM132A, a novel Wnt signaling pathway regulator through Wntless (WLS) interaction, B. Li et al., 2020, Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology, Vol. 8, 599890.
https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2020.599890
FAQ
-
What is Biotin‑Azide Plus used for?
Biotin‑Azide Plus is a reagent for biotinylating biomolecules via copper‑catalyzed azide–alkyne cycloaddition (CuAAC). It enables efficient biotin labeling under very low copper concentrations, making it suitable for sensitive peptides, proteins, nucleic acids, and cellular applications.
-
How does Biotin‑Azide Plus differ from standard biotin‑azides?
Unlike conventional biotin‑azide reagents, Biotin‑Azide Plus contains an Azide‑Plus linker, a built‑in copper‑chelating moiety that:
- accelerates the CuAAC reaction
- stabilizes Cu(I) to prevent side reactions
- enables efficient labeling with less added copper
- reduces or eliminates the need for external ligands like THPTA
This makes the reagent ideal for biomolecules that are copper‑sensitive or easily degraded.
-
Is Biotin‑Azide Plus suitable for copper‑free SPAAC reactions?
No. The Azide‑Plus linker provides benefits only in CuAAC reactions.
For copper‑free SPAAC, the preferred alternative is Biotin‑PEG4‑Azide, which is more cost‑effective and compatible with DBCO, BCN, and other strained alkynes.
-
What biomolecules can be labeled using Biotin‑Azide Plus?
Biotin‑Azide Plus can be used to label a wide range of terminal alkyne‑modified targets, including:
- peptides and proteins
- nucleic acids (DNA, RNA, oligos, mRNA)
- polysaccharides
- viruses and viral particles
- biomolecules used in cell‑based assays
It is compatible with most commercially available alkyne‑modified substrates.
-
What is biotin and why is it used in research?
Biotin (vitamin B7) forms one of the strongest known non‑covalent interactions with streptavidin and avidin.
This interaction is widely used for:
- affinity purification
- protein enrichment
- imaging and detection assays (ELISA, Western Blot, IHC)
- surface immobilization for binding assays
- enrichment of newly synthesized proteins for MS analysis
- nucleic‑acid purification and detection (ISH, Southern, Northern blots)
Streptavidin is typically preferred over avidin due to higher solubility and lower nonspecific binding.
-
Why use click chemistry for biotin labeling?
Click chemistry provides:
- highly selective, bioorthogonal reactions
- precise control of labeling position
- fast and efficient reaction rates
- compatibility with proteins and nucleic acids
- mild reaction conditions that preserve biomolecule integrity
Unlike NHS‑ester labeling, click chemistry allows site‑specific biotin attachment only where an alkyne is present.
-
What are the key advantages of Biotin‑Azide Plus?
- Efficient biotin labeling with minimal copper
- Built‑in copper‑chelating functionality
- Faster reaction kinetics
- Reduced copper‑induced damage to sensitive samples
- Highly stable triazole linkage
- Excellent compatibility with peptides, proteins, and nucleic acids
-
Does Biotin‑Azide Plus require a copper‑chelating ligand?
Usually no. The Azide‑Plus moiety chelates copper ions directly, providing catalytic activity and stability. This allows reactions to proceed even with low Cu(I) concentrations and without mandatory THPTA ligands.
-
How stable is the resulting biotin linkage?
CuAAC forms a stable triazole bond that is resistant to physiological conditions, organic solvents, heat, and enzymatic degradation.
The biotin–streptavidin complex formed afterwards is one of the strongest non‑covalent interactions known.
-
How should Biotin‑Azide Plus be stored?
Store at –20 °C, protected from light and moisture. Avoid repeated freeze–thaw cycles to preserve reagent performance.
-
Is Biotin‑Azide Plus compatible with living cells?
CuAAC requires copper, which is not ideal for live‑cell labeling.
For live cells or highly sensitive systems, copper‑free SPAAC reagents such as Biotin‑PEG4‑Azide or DBCO‑biotin derivatives are recommended.

