
In Vivo EdU Cell Proliferation Assay for Imaging
ClickTech In Vivo EdU Cell Proliferation Kit for Imaging
| Size | Catalog No. | Price |
|---|---|---|
| Dye 488 / 100 Assays / Size S | BCK-EdU488IM100+IV-S | € 530,00 |
| Dye 488 / 100 Assays / Size M | BCK-EdU488IM100+IV-M | € 665,00 |
| Dye 488 / 100 Assays / Size L | BCK-EdU488IM100+IV-L | € 810,00 |
| Dye 555 / 100 Assays / Size S | BCK-EdU555IM100+IV-S | € 530,00 |
| Dye 555 / 100 Assays / Size M | BCK-EdU555IM100+IV-M | € 665,00 |
| Dye 555 / 100 Assays / Size L | BCK-EdU555IM100+IV-L | € 810,00 |
| Dye 594 / 100 Assays / Size S | BCK-EdU594IM100+IV-S | € 530,00 |
| Dye 594 / 100 Assays / Size M | BCK-EdU594IM100+IV-M | € 665,00 |
| Dye 594 / 100 Assays / Size L | BCK-EdU594IM100+IV-L | € 810,00 |
| Dye 647 / 100 Assays / Size S | BCK-EdU647IM100+IV-S | € 530,00 |
| Dye 647 / 100 Assays / Size M | BCK-EdU647IM100+IV-M | € 665,00 |
| Dye 647 / 100 Assays / Size L | BCK-EdU647IM100+IV-L | € 810,00 |
Chemical Properties
-
Shelf Life
12 months unopened after receipt
-
Storage Conditions
2-8 °C
-
Physical State
kit system made of different components
-
CAS Number
n.a.
-
Excitation (max)
Dye 488: 496 nm | Dye 555: 546 nm | Dye 594: 584 nm | Dye 647: 643 nm
-
Emission (max)
Dye 488: 516 nm | Dye 555: 579 nm | Dye 594: 603 nm | Dye 647: 662 nm
-
Ɛ (max)
Dye 488: 83.000 cm-1M-1 | Dye 555: 91.000 cm-1M-1 | Dye 594: 110.000 cm-1M-1 | Dye 647: 250.000 cm-1M-1
-
Preparation/Handling
please see user manual of the kit
Product Information
What is EdU Assay?
The EdU (5-ethynyl-2′-deoxyuridine) assay is a modern method for detecting cell proliferation by labeling newly synthesized DNA. During DNA replication, EdU is incorporated into DNA in a partial replacement of thymidine. Its specific chemical properties enable it to be detected via a gentle ‘click chemistry’ reaction, allowing proliferating cells to be visualized without the need for harsh treatments.
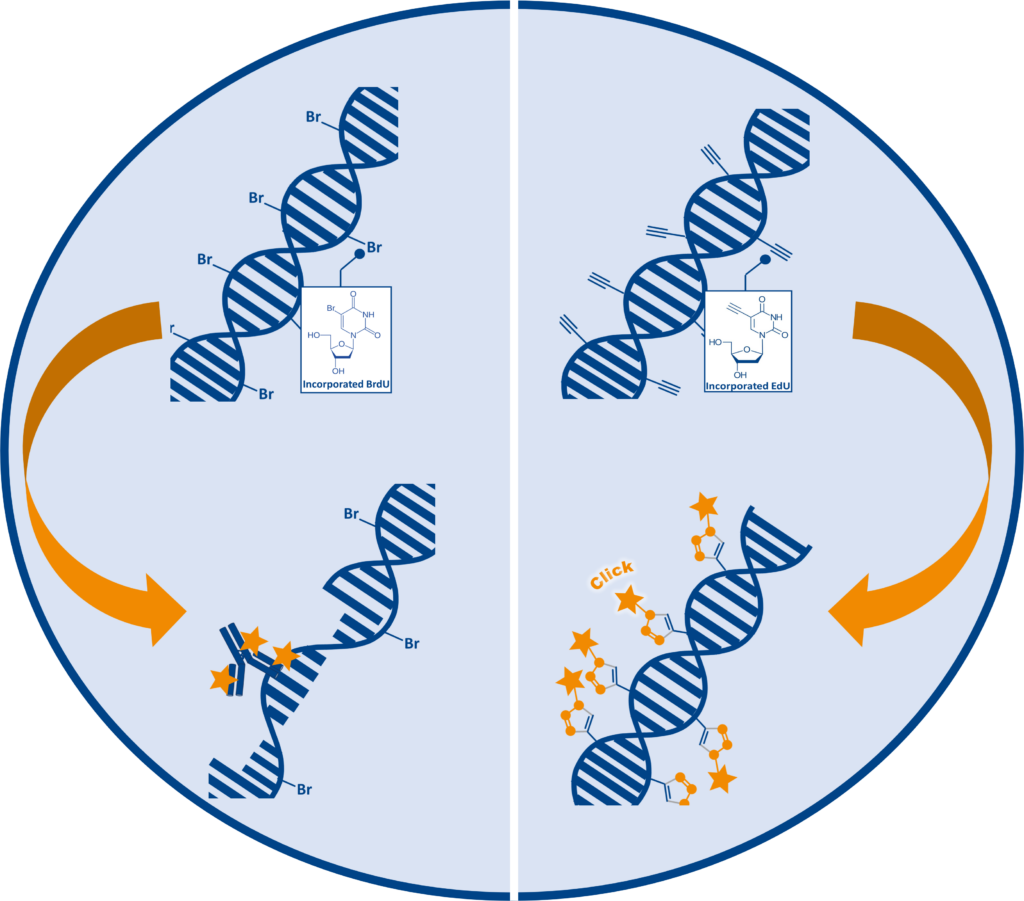
Compared to traditional BrdU assays, which require DNA denaturation for antibody access, EdU detection is faster, antibody-free, and preserves sample morphology. This makes it ideal for high-resolution imaging and multiplex applications in both cell culture and in vivo systems.
New Feature:
All imaging kits now include DAPI for nuclear counterstaining, enabling simultaneous visualization of DNA synthesis and nuclear morphology. This enhancement supports improved segmentation and staging of replicating cells, especially in imaging-based workflows.
In vivo EdU Cell proliferation assay for imaging: What is it?
Analyze cellular proliferation in whole organisms without harsh denaturation steps
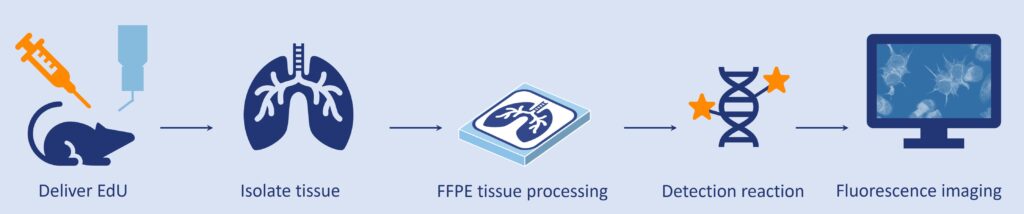
The ClickTech in vivo EdU Cell proliferation assays for imaging are an evolvement of EdU cell proliferation assays designed specifically for usage with whole organisms. The kit include increased EdU quantities and optimized reagents to support systemic labeling of dividing cells in vivo, enabling the analysis of biological processes such as tumor growth, neural and tissue development, and cellular regeneration.
On the contrary to BrdU, which requires DNA denaturation under harsh conditions (e.g. acid, heat, or enzymatic digestion), EdU assay enable chemistry preserves tissue morphology and antigenicity — offering a much gentler alternative for in vivo use.
EdU is incorporated into replicating DNA and can be administered through various methods, depending on the model organism:
- Injections: intraperitoneal, intramuscular or subcutaneous
- dissolved in drinking water: for continuous systemic delivery
- direct incubation e.g. zebrafish larvae
After incorporation, Edu labeled cells are visualized using a fluorescent dye through the highly specific copper-catalyzed click chemistry reaction CuAAC.
Difference between standard EdU cell proliferation kits for imaging and in vivo kits
Standard baseclick´s EdU cell proliferation assays are optimized for in vitro cell culture, where the concentrations of EdU and the protocols used are insufficient for labeling whole organisms. If researchers plan to follow cell proliferation in organism different protocols and higher amounts of EdU are needed. The ClickTech In vivo Kit addresses this with:
- Additional EdU for systemic administration
- Protocols adapted for in vivo labeling and tissue preparation
- Detection reagents tailored for animal or tissue sample analysis
- Format options for different experimental scales
- Now includes DAPI for nuclear counterstaining in imaging workflows
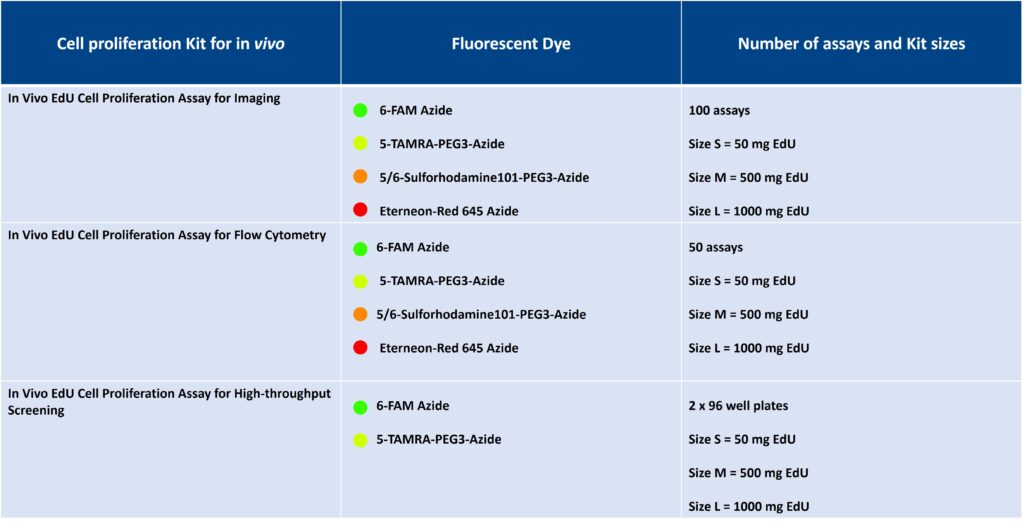
baseclick is offering in vivo kits not only for EdU cell Proliferation kit for Imaging but also for other EdU cell proliferation variants as flow cytometry or high throughput screening for various wavelengths.
What does the user gain?
ClickTech in vivo EdU Cell proliferation assays for imaging provide the customer with the advantage to have an all-in-one product in combination with protocols for both labeling of the organism and for analyzing the sample. EdU and its mild labeling conditions preserve tissue integrity.
Researchers also benefit from a reduced price when purchasing the in vivo variant instead of the ClickTech EdU Cell proliferation assay for imaging, when used in combination with additional EdU.
Features & Applications
- Suitable for imaging in mice, rats, zebrafish, and more
- Compatible with injection, water-based delivery, or incubation
- Antibody-free, fast detection (~30 minutes)
- Works with multiplex labeling and co-staining
- Analyzes S-phase activity in intact tissues
Optimization Tips
- Longer incubation → lower EdU concentration recommended
- If no EdU protocol exists, use BrdU-based references to optimize
- Lower EdU can yield comparable fluorescence to BrdU
LITERATURE
An efficient protocol for in vivo labeling of proliferating epithelial cells, C. Michel et al., 2018, J. Immunol. Methods, Vol. 457, p. 82-86.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jim.2018.03.015
Cisplatin-induced DNA double-strand breaks promote meiotic chromosome synapsis in PRDM9-controlled mouse hybrid sterility, L. Wang et al., 2018, eLife, Vol. 7, p. e42511.
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.42511
FXR Regulates Intestinal Cancer Stem Cell Proliferation, T. Fu et al., 2019, Cell, Vol. 176, p. 1098-1112.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2019.01.036
Nuclear morphology is a deep learning biomarker of cellular senescence, I. Heckenbach et al., 2022, Nat Aging, Vol. 2, p. 742–755.
https://doi.org/10.1038/s43587-022-00263-3
P21-Activated Kinase Inhibitors FRAX486 and IPA3, Martin Hennenberg et al.,2016, PMCID: PMC4829229 PMID: 27071060
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0153312
FAQ
-
What type of cells can incorporate EdU?
The EdU cell proliferation assay has been applied to many different cell types and organisms from prokaryotic to eukaryotic. Cell lines such as E. coli, HeLa, HEK, MOLM are arguably among the most routine applications, but also animals, like mouse, rat, the nematode C. elegans, crickets (Gryllus bimaculatus), chicken (Gallus domesticus) and zebra fish (Danio rerio) or even plants (e.g. Arabidopsis thaliana) can be applied.
Cells that possess a pyrimidine pathway that can phosphorylate EdU to the corresponding triphosphate, which is then accepted by the host DNA polymerase for incorporation into DNA during replication. -
Can I perform EdU cell proliferation detection on living cells?
EdU is incorporated into living cells, but the detection reaction must be performed on fixed and permeabilized samples.
-
How does EdU labeling compare to BrdU or the 3H-thymidine incorporation assay?
All three methods enable to determine cell proliferation directly by incorporation of a metabolite analogue and subsequent detection. The 3H-thymidine incorporation assay is very sensitive, but the radioactive compound requires specialized equipment and dedicated lab space for handling. EdU and BrdU assays are non-radioactive alternatives with decreased risk for health and environment. Compared to the BrdU incorporation assay the EdU assay is more sensitive, requires less handling time and needs no harsh DNA denaturing conditions for detection. Therefore, the EdU cell proliferation is also compatible with multiplexing.
-
Can I combine DAPI staining and EdU detection?
Yes, this is feasible. Please note that DAPI staining should be done after the click detection step. Alternatively, SYBR Green DNA staining can be used. But, please note that SYBR green should not be used with dyes of 488 nm wavelengths.
-
When can I safely interrupt the experiment?
It is possible to safely interrupt the protocol after the fixation step. Thereto, remove the fixation solution and wash as suggested by the user manual, then the cells can be stored in buffer at 4° C. Alternatively, the experiment can also be safely interrupted after permeabilization, again as described above.
Please note: It is important to proceed with the experiment if the click cocktail for the detection of the EdU has been prepared already. -
Is antibody staining compatible with the EdU?
Antibody staining is compatible with EdU cell proliferation detection when antibody detection is done after the click detection step. Please be aware of the dye used for EdU detection. Check also the user manual for more information.
-
How to determine the EdU incubation time?
The EdU incubation time depends on the cell type or organism, the applied EdU concentration and the experimental design. For a start it is advisable to refer to a literature protocol (which is close to your experimental setup) and to test the conditions with a low number of samples. As a general guideline we recommend to use a maximum of 10 µM final EdU in the cell culture medium for incubations. For longer incubation (> 1 day) the concentration should be decreased to 1-5 µM.

