
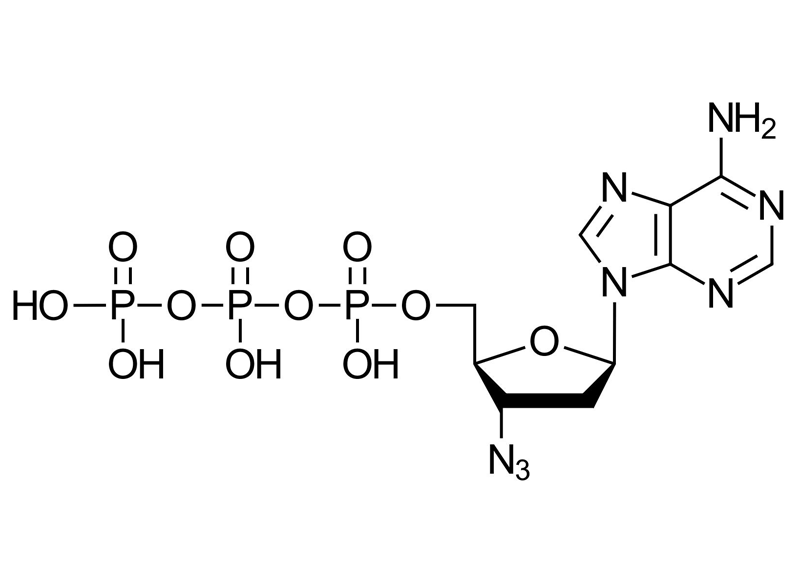
3′-Azido-2′,3′-ddATP
Triphosphate for modifying of 3'END RNA or ssDNA
| Size | Catalog No. | Price |
|---|---|---|
| 1 µmol | BCT-25-S | € 250,00 |
| 5 µmol | BCT-25-L | € 850,00 |
Chemical Properties
-
Molecular Formula
C10H15N8O11P3
-
Shelf Life
12 months unopened after receipt
-
Storage Conditions
-20 °C
-
Molecular Weight
516.19 g/mol
-
Purity
≥ 98% (HPLC)
-
Physical State
100 mM clear aquaeous solution; colorless
-
CAS Number
1383937-03-8 (sodium salt)
92562-94-2 (free acid)
-
Absorption (max)
λmax = 258 nm
-
Ɛ (max)
15,400 cm-1 M-1
Product Information
A Nucleotide Analogue for the Selective 3´End Labeling of Nucleic Acids via Click Chemistry or Staudinger Ligation
Molecular Structure and Applications of 3′-Azido-2′,3′-ddATP
3′-Azido-2′,3′-ddATP is a chemically modified analogue of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) featuring an azido (N₃) group in place of the 3′OH group of the sugar moiety. This modification enables
- Copper-catalyzed azide–alkyne cycloaddition
- Copper-free strain-promoted azide–alkyne cycloaddition (SPAAC)
for highly efficient labelling via click chemistry.
The absence of a 3′OH group makes 3′-azido-2′,3′-ddATP a chain-terminating nucleotide in polymerization reactions such as the IVT reaction. Unlike other internal labeling DNA or RNA nucleotides (e.g., EdUTP or EUTP), this analogue is ideal for site-specific, post-synthetic introduction of a single azido group at the 3′end of nucleic acids using enzymes like Poly(A) polymerase or terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT).
Biorthogonal Azide Functionality
The azido group is a biorthogonal functionality, meaning it does not interfere with natural biomolecules. It reacts selectively with:
- Alkynes → forming triazoles via CuAAC or SPAAC
- Phosphines → forming amides via Staudinger ligation
Both reactions meet the criteria of click chemistry, and the development of azide–alkyne cycloaddition was recognized with the 2022 Nobel Prize in Chemistry.
Performance with Reverse Transcriptase
3′-Azido-2′,3′-ddATP is efficiently incorporated by reverse transcriptases during cDNA synthesis. Due to its chain-terminating property, elongation stops immediately after incorporation, enabling controlled fragment generation. This feature is exploited in ClickSeq NGS workflows, where azido-ddNTPs are used to create precise fragment ends for click-based adapter ligation instead of enzymatic ligation.
Advantages in RT reactions:
- Controlled termination for sequencing
- Compatible with click chemistry for primer or adapter conjugation
- Reduces ligation artifacts and improves reproducibility in RNAseq libraries
Detailed protocols for the 3′end modification of nucleic acids using 3′-azido-2′,3′-ddATP, and for the attachment of fluorescent dyes, biotins, linkers, and cell-targeting ligands via click chemistry are available from baseclick.
This technique has been used by baseclick and ClickSeq technologies to develop new sequencing kits designed to eliminate common bottlenecks and artifacts in standard RNA-sequencing workflows, such as sequence chimeras, recombination, fragmentation bias, and ligation inefficiencies. All this was achieved while preserving library complexity and improving reproducibility. In this kit not only 3′-Azido-2′,3′-ddATP is used as a stop nucleotide, also the structural identical analog triphosphates for C, G and T are used.
Application areas for 3′-Azido-2′,3′-ddATP
- 3′-End Labeling of Nucleic Acids: Incorporation into ssDNA or mRNA followed by click conjugation with dyes, biotin, or ligands.
- Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS): Used in ClickSeq kits as a chain terminator for generating azido-modified fragments, enabling primer conjugation without enzymatic ligation.
- Functional Studies: Potential inhibitor of telomerase activity, offering applications in cancer research by limiting cell division through telomere shortening.
- Advanced Bioconjugation: Enables attachment of sugars or targeting moieties for active transport into cells.
3`-Azido-2`,3´-dideoxyadenosine 5`-triphosphat is mostly used for labeling of nucleic acids. Here the molecule is incorporated enzymatically to the 3`end of a nucleic acid, mostly ssDNA or mRNA, and afterwards the azido group can be used for chemical modifications by click chemistry. But the functionality of this azido modified dideoxy nucleotide is not limited to that, through to its function as chain terminating nucleotide it can be used for sequencing similar to Sanger sequencing when added as nucleotide during reverse transcription or cDNA synthesis. Through the possibility to use click chemistry for modification of the azide, a primer can be clicked to a terminated nucleic acid, enabling primer conjugation without the need for enzymatic ligation as used for most other next generation sequencing (NGS) methods.
Advantages
- Site-specific labeling at the 3′ end
- Compatible with enzymatic incorporation using Poly(A) polymerase, TdT, and reverse transcriptase
- Supports copper-free click chemistry for sensitive biomolecules
- Chain-terminating property useful for sequencing and controlled fragment generation
Protocols and Resources
baseclick provides detailed protocols for:
- 3′-End modification of nucleic acids using 3′-Azido-2′,3′-ddATP
- Click conjugation with fluorescent dyes, biotin, linkers, and targeting ligands
LITERATURE
Site-specific terminal and internal labeling of RNA by poly(A) polymerase tailing and copper-catalyzed or copper-free strain-promoted click chemistry, M. L. Winz et al., 2012, Nucleic Acids Res., Vol. 40, p. 1–13.
https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gks062
Chemoenzymatic Preparation of Functional Click-Labeled Messenger RNA, S. Croce et al., 2020, ChemBioChem, Vol. 21, p. 1641-1646.
https://doi.org/10.1002/cbic.201900718
Application and design considerations for 3′-end sequencing using click-chemistry, M. K. Jensen et al., 2021, Methods in Enzymology, Vol. 655, p. 1-23.
https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.mie.2021.03.012
Efficient DNA Click Reaction Replaces Enzymatic Ligation, M. Kollaschinski et al., Bioconjugate Chemistry, 2019.
https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.9b00805
FAQ
-
What is 3′-Azido-2′,3′-ddATP used for?
It is primarily used for site-specific 3′-end labeling of nucleic acids via click chemistry or Staudinger ligation. It also serves as a chain terminator in sequencing workflows such as ClickSeq.
-
Can this nucleotide be incorporated internally into RNA or DNA?
No. Due to the absence of a 3′-OH group, it acts as a chain terminator and cannot introduce internal azido groups.
-
Which enzymes can incorporate 3′-Azido-2′,3′-ddATP?
Commonly used enzymes include Poly(A) polymerase, terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT), and reverse transcriptase for controlled termination.
-
How does it perform with reverse transcriptase?
It is efficiently incorporated and stops elongation immediately, enabling controlled fragment generation for sequencing and click-based adapter ligation.
-
Is it compatible with copper-free click chemistry?
Yes. The azido group supports SPAAC reactions with strained alkynes (e.g., DBCO) for copper-free labeling.
-
What are typical applications?
mRNA and ssDNA labeling, NGS workflows (ClickSeq), Primer conjugation without enzymatic ligation, Telomerase inhibition studies.
-
Is this product for diagnostic or therapeutic use?
No. It is for Research Use Only (RUO).

